
A service grip dead end is a type of hardware used to terminate at a specific location along the transmission line. This is mainly done at points where the conductor undergoes a change in direction. It plays an important role in mechanical integrity of overhead transmission lines. This helps to contribute to the safe and efficient transmission of electrical power. Its design and application align with industry standards. This is to ensure the reliability of the transmission system. It is from durable materials that help resist rust and corrosion from the various environmental aspects. These materials include galvanized steel, aluminum alloy, composite materials and stainless steel. Common types include automatic dead ends, compression dead ends, helical dead ends, spiral and tension dead ends. They find use in various applications such as service drops, guyed structures, mid-span applications and secondary lines.
Key features of service grip dead end
Service grip dead end is a crucial component designed to securely terminate conductors. This helps to contribute to the stability and reliability of the transmission system. It has various features that help ensure their popularity in the industry. The following are the features of the service grip dead end.
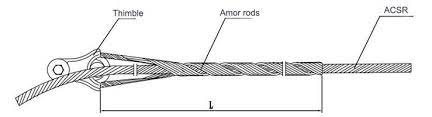
- Tension control – proper tension control helps to maintain the desired sag. It also prevents excessive stress on the transmission line.
- Adjustability and flexibility – adjustability helps to ensure the proper fitting to the conductor. It also simplifies installation and accommodates variations in transmission line.
- Protection against abrasion – the dead ends provide protection against abrasion and wear.
- Compatibility – this allows for versatility in transmission lines designs without need for different types of hardware.
- High quality materials – they are from durable materials that ensures the strength and longevity of dead ends. This helps to contribute to their reliability in demanding transmission environments.
- Secure conductor termination – the dead ends securely terminates conductors at specific points along the transmission line.
- Resistance to environmental conditions – this helps to ensure the longevity and reliability of dead ends.
- Gripping mechanisms – this feature helps to prevent conductor slippage. This is to ensure a secure and reliable termination point without the risk of unintentional detachment.
- Ease of maintenance – regular maintenance helps to ensure the continued effectiveness of dead ends.
Selection and installation of service grip dead ends
The selection process of the service grip dead ends involves consideration of various factors. This is to ensure the selected dead end meets the specific requirements of the project. These factors include considering project requirements, industry standards, dead ends types, adjustability, tension control requirements and budgets. The installation process should assist to ensure a secure and reliable termination of conductors. The following is a general installation process of the service grip dead end.
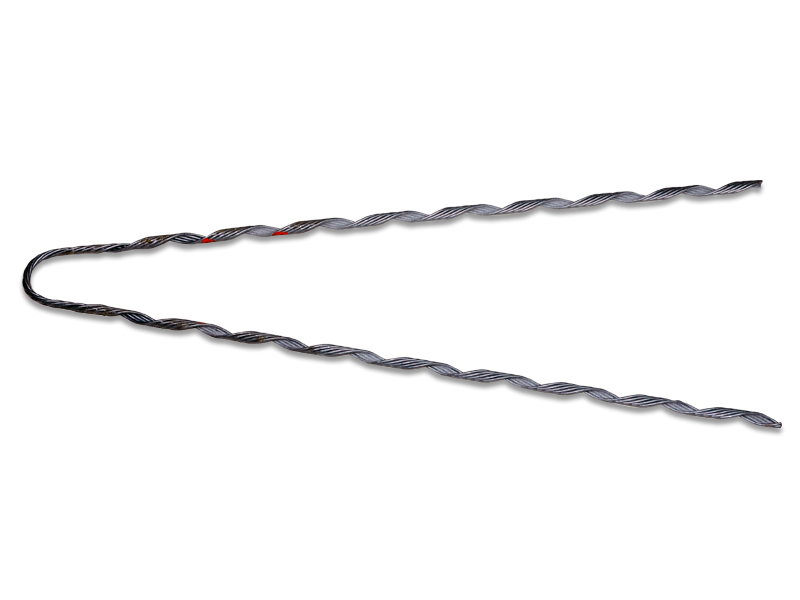

- Preparation – gather all the necessary tools and equipment required for the installation. This is including suitable wrenches, tensioning devices and any specialized tools.
- Dead end compatibility – confirm the selected dead ends are compatible with the conductor size and type used in the transmission line.
- Dead ends inspection – inspect the service grip dead ends for any visible defects. Confirm all the conductors are in good condition before installation.
- Conductor preparation – prepare the conductor by removing any debris, contaminants or corrosion.
- Dead end positioning – position the service grip dead end at the desired location. Ensure it is properly aligned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Dead end attachment – attach the dead end to the conductor by following the instructions for securing the grip around the conductor. Use the recommended bolts, nuts or other fastening mechanisms.
- Tension – apply the necessary tension to the conductor according to he projects specifications. Use the suitable devices to achieve the desired tension levels.
- Alignment verification – verify that the dead end aligns properly and that the conductor is securely held in place.
- Inspect the installation – perform a visual inspection of the entire installation. Check for signs of damage, misalignment and other issues.
- Documentation – maintain detailed records of the installation process. This is including adjustments made, tension levels achieved and other observations.
Maintenance and inspection of service grip dead ends
Regular maintenance and inspection of service grip dead ends helps to ensure the continued reliability and performance of the system. It also helps to identify and address potential issues that could lead to accidents. Additionally, it is advisable to conduct periodic professional inspections and maintenance once in a while. The following is a basic guide for maintenance and inspection in South America.
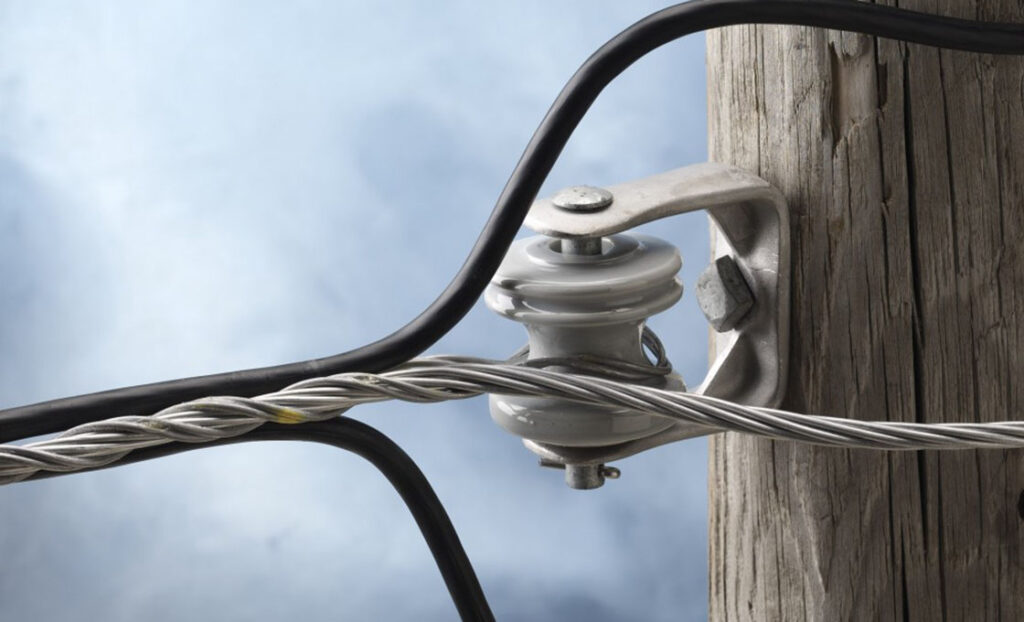

- Schedule regular visual inspections of service grip dead ends to identify any visible signs of wear, damage or corrosion.
- Periodically clean the service grip dead ends to remove dust, debris and environmental contaminants. It also helps to maintain the integrity of the components and prevent the accumulation of materials that lead to corrosion.
- Conduct checks on bolts, nuts and other fastening mechanisms for proper tightness. Tis also helps to ensure all the components are securely fastened to prevent loosening.
- Apply corrosion resistant coatings to protect the dead ends from the corrosive effects of environmental elements.
- Lubricate moving parts and joints to ensure smooth operation of any moving components and reduce friction.
- Check for the presence of bird nests to prevent any foreign objects from interfering with the functionality.
- Confirm the tension in the conductor is within the specified range. Use the suitable tension measuring devices.
- Ensure the dead ends are properly aligned with the conductor and make the necessary adjustments if required.
- Perform tests to ensure the features operate as intended.
- Maintain detailed records of inspections including findings and any corrective actions taken.
Comparative analysis of service grip dead ends in South America
Conducting a comparative analysis involves assessing and evaluating different types and designs of the service grip dead end. It may include consulting market reports, industry analyses or manufacturers information. Additionally, it is important to consult with industry experts for proper selection of the dead end. The following are the factors to include in the comparative analysis in South America.
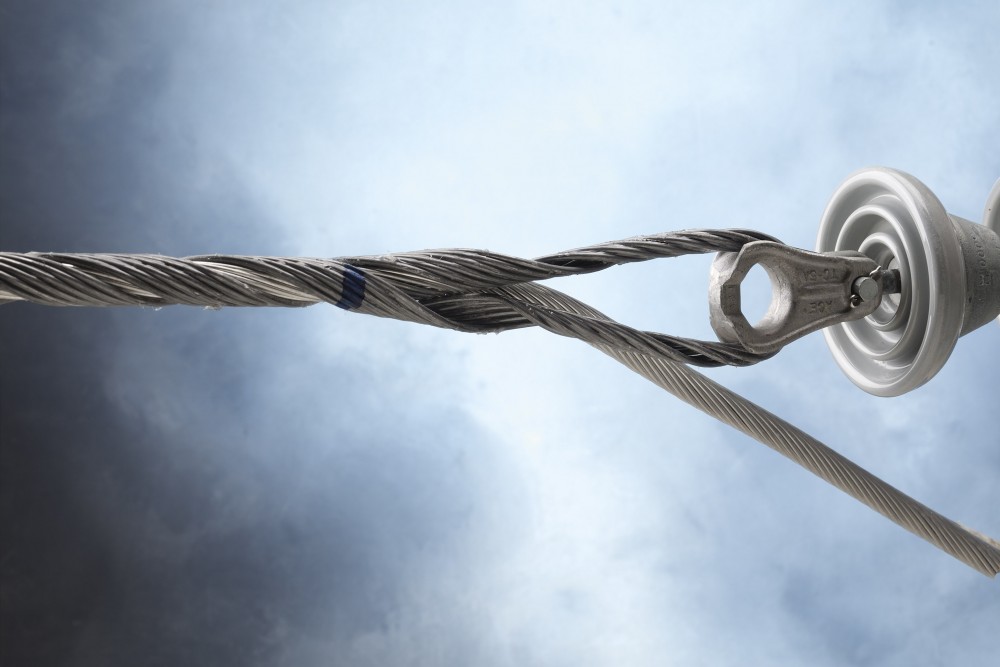

- Technical support – evaluate the availability and responsiveness of technical support provided by manufacturers.
- Costs – compare the costs of service grip dead ends from the various manufacturers. Consider the overall value including features, durability and extra services offered.
- Performance and durability – examine the performance and durability of the service grip dead ends. Check their resistance to corrosion, high winds and temperature variations.
- Market players – identify the key manufacturers and suppliers of service grip dead ends in South America. Compare their market share, reptation and range of products offered.
Certifications and standards in South America
These standards and certifications of service grip dead ends vary depending on the specific region of installation. Power transmission industry adheres to international standards applied for service grip dead ends. Additionally, it is important to ensure the selected dead end meets the relevant industry standards. The following are the common standards in South America.
- IEC standards – these are standards for composite suspension and tension insulators for transmission systems. It includes test, methods and acceptance criteria.
- ANSI standards – these are standards for test methods for electrical power insulators and wet-process porcelain insulators.
- ISO certifications – this offers standards for quality management systems and environmental management systems.
- ASTM standards – this includes the standard test method for bulk density.
- Country specific standards – each South American country has its own set of standards and certifications relevant to power transmission equipment. Most common include ANEEL in Brazil, ENRE in Argentina and SEC standards in Chile.
Regional market for service grip dead end in South America
There are various market trends and dynamics that influence the regional market for service grip dead ends. These include market dynamics, supplier availability and local manufacturing. Additionally, it is important to conduct market research to understand the various aspects that influence demand for dead ends in the region. The following are the factors that shape the regional market for service grip dead ends in South America.
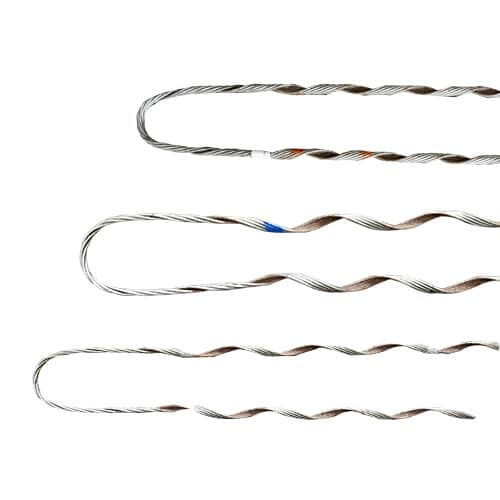

- Technological advancements – there may be higher opportunities for manufacturers offering technologically advanced service grip dead ends.
- Environmental conditions – the diverse environmental conditions in the region influence the demand for service grip dead ends.
- Investments in infrastructure – investments in transmission and distribution infrastructure impacts the market for service grip dead ends.
- Replacement and upgradation projects – this may create opportunities for the installation of modern and more efficient service grip dead ends.
- Renewable energy integration – increased focus on renewable energy sources and integration contributes to the demand for reliable transmission infrastructure.
Frequently asked questions
A service grip dead end is responsible for securing the neutral conductor and prevent it from unwinding. It plays a vital role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the grid.
Service gip dead ends prevent the neutral conductor from loosening to maintain consistent voltage levels and prevent power outages. It also helps to reduce stress especially in south American wide range of terrains.