
A cross plate anchor is an anchor used to provide stability and support various structures with heavy loads or forces. It consists of a plate with arms arranged in a cross shape to help distribute the load and anchor the structure securely. A cross plate anchor is also known as a guy plate or anchor plate. It helps in soil stabilization and securing objects to the ground. The design of the cross plate anchor helps to maintain the structural integrity of the overhead transmission lines. It is from materials strong materials that ensure strength and durability of the anchors. Cross plate anchor is a technology that secures the backbone of the national electrical network in most of south American countries. Examples include standard cross plate anchor, helical cross plate anchor and rock anchor. They find use in transmission towers, telecommunication lines, wind turbines and slop stabilization.
Key features of cross plate anchor
Cross plate anchors contributes to the effectiveness in providing stability in various applications. The features also ensure the popularity of the cross plate anchors in various anchors. The following are the common features of the anchors.
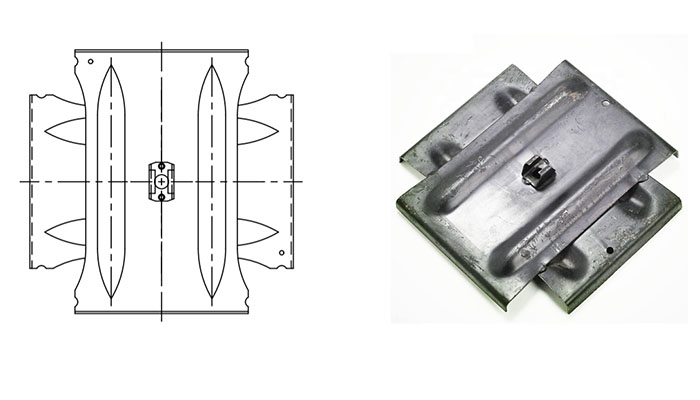
- Cross-shaped design – the shape of the anchor provides multiple arms to distribute the load and tension over a larger area. This design helps to enhance the stability and prevent localized stress points.
- Corrosion resistance – the anchor has coatings are from materials that resist corrosion for various outdoor applications.
- Ease of installation – most of the cross-plate anchors are easy to install and provide simple installation features.
- Load-bearing capacity – the load bearing capacity ensures the anchor effectively support the structures.
- Cost effectiveness – their ease of installation and adaptability contributes to their economic feasibility.
- Material strength – the anchors are from sturdy materials such as steel to ensure the strength and durability.
- Design – the anchors are available in multiple designs to suit different applications and soil conditions.
- Adaptability – the anchors are suitable for various soil conditions including rocky, sandy or soft soils.
Selection of cross plate anchors
Proper selection of cross plate anchors is crucial to ensure the anchor meets the specific application needs. It involves considering various factors to ensure it is suitable for various applications. These factors include soil conditions, load requirements, environmental factors, installation depth and terrain characteristics. The installation process involves several steps to ensure their proper placement and effectiveness. This is in providing stability and reliability. The following includes the step-by-step installation process of the cross plate anchor.
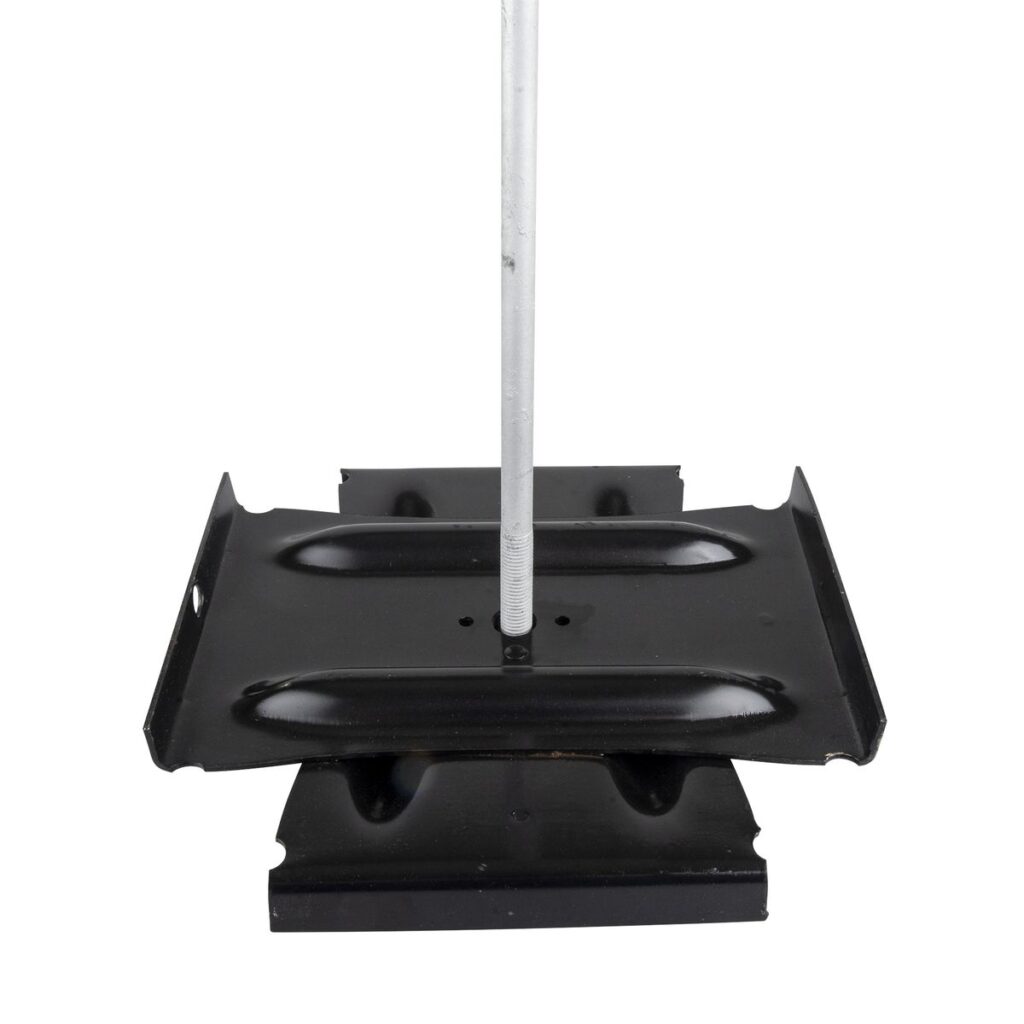

- Site assessment – perform a site assessment to understand the soil conditions, load requirements and environmental factors.
- Select the right anchor type – choose the type of cross plate anchors that is most suitable for soil conditions and load bearing requirements.
- Prepare the anchor – prepare the anchor to ensure it meets the manufacturers guidelines.
- Location – mark the exact location where the cross plate anchor will install. This should be in accordance with engineering plans.
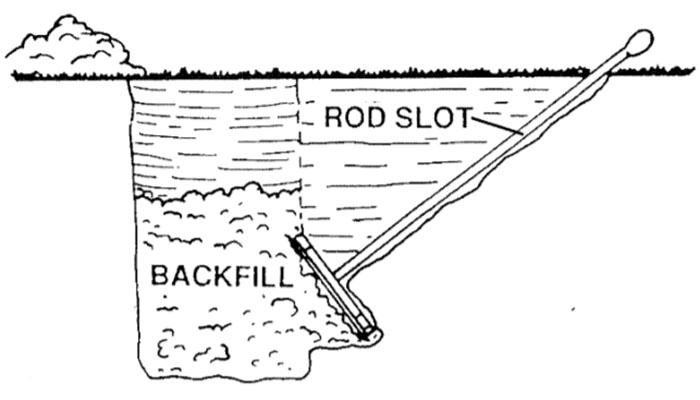
- Hole excavation – excavate the hole at the marked location where the depth depends on the anchor type and soil conditions.
- Anchor installation – for a screw-in anchor, rotate the anchor into the soil using suitable equipment. For standard cross plate anchors, embed the anchor in the excavated hole.
- Backfill – backfill the hole with the soil and compact it to provide extra stability. This is following proper compaction procedures. This is to ensure the soil is densely packed around the anchor.
- Guy wire attachment – attach the guy wires securely to the anchor and ensure proper tensioning of the guy wires.
- Verify alignment and tension – ensure proper alignment and tensioning of the top tie. This is to enhance the anchors performance and overall stability.
- Inspection – perform a final inspection of the installed anchor and surrounding areas.
- Documentation – keep details of the installation process including the depth, alignment and tensioning.
Maintenance and inspection of cross plate anchors
Regular maintenance and inspection of the anchors helps to ensure their continued stability. The diverse soil conditions of the region define the frequency of maintenance and inspection. Additionally, refer to specific project plans, engineering guidelines and safety regulations during the maintenance process. The following is a basic guide for maintenance and inspection for cross plate anchors.
- Establish a regular inspection schedule based on industry standards, environmental conditions and regulatory requirements.
- Conduct a visual inspection of each cross plate anchors to identify any signs of wear, corrosion of physical damage.
- Check the condition of the anchor for signs of corrosion and address and repair anu areas compromised.
- Inspect the fasteners, nuts and bolts for proper tightness and replace any components showing signs of wear such as washers or nuts.
- Verify the load bearing capacity of the cross plate anchor to ensure it can withstand the tension and loads.
- Inspect the concrete for cracks, deterioration and any signs of structural compromise.
- Address any vegetation growth around the cross plate anchor that could compromise its integrity and trim as needed.
- Consider the specific environmental conditions in South America. This is including humidity and temperature variations.
- Maintain detailed records of each inspection including findings, any maintenance performed and dates of inspections.
Comparative analysis of cross plate anchors in South America
Conducting a comparative analysis f cross plate anchors involves considering various factors. These include regional differences, soil conditions, applications and the effectiveness of each type. It also helps to ensure proper selection of the cross plate anchors for various applications. Additionally, it is important to seek professional help for proper selection. The following are the key factors to include in the comparative analysis in South America.

- Soil conditions – regions with diverse soil types including tropical soils anchors need to adapt to variations in soil composition.
- Applications – cross plate anchors find use in various applications. This is including power transmission lines and renewable energy. The selected anchor should ensure stability and reliability in various terrains.
- Infrastructure development – development of urban areas and remote regions may influence the need for ease of transport and installation.
- Technological advancements – differences in technological infrastructure impacts the adoption of the latest anchor technologies.
- Government initiatives – the initiatives promote renewable energy growth. This leads to different anchor requirements.
- Environmental factors – South America has a wide range of environmental factors. This is including high humidity and coastal areas.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are various certifications and standards for cross plate anchors in South America that govern their use. These factors depend on regional regulatory bodies, industry associations and engineering codes. Also, it is important to consult the specific standards and certifications relevant to the country and industry. The following are the certifications and standards in South America.

- ISO standards – these are standards related to anchors for ground anchorage. This is to ensure international best practices.
- National standards – these are various electrical codes and technical standards for anchors in various countries.
- Geotechnical standards -these are standards related to geotechnical engineering. This is including those applicable to anchor systems.
- Seismic standards – these standards may include seismic design provisions that impact anchor requirements.
- Wind load standards – the standard may include provisions for wind loads affecting anchor specifications.
- Material standards – this is a standard that helps to ensure the use of quality and durable materials for the anchor.
- Environmental certifications – these help to ensure the eco-friendly installations and maintenance of anchors.
- Quality control standards – these are standards such as ISO that are applicable to manufacturers and suppliers.
Regional market for cross plate anchors in South America
The demand of the cross plate anchors depend on various factors such as infrastructure development, construction projects and the growth of the industries. Main players in the market include Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Peru, Colombia and Venezuela among others. Additionally, manufacturers and suppliers should observe the market trends and dynamics that influence the demand and availability. The following are the factors that shape the regional market for cross plate anchors in South America.
- Construction and energy sector – this includes renewable energy projects and telecommunication infrastructure which drives the demand for cross plate anchors.
- Transmission and telecommunication – the demand for cross plate anchors may arise from the construction of power transmission lines.
- Infrastructure development – the development of roads and buildings contribute to the demand for anchor systems.
- Infrastructure projects – cross plate anchors help in construction of transmission towers, bridges and other developments.
- Renewable energy – the anchors also support the wind turbines and solar installations help support renewable projects in the region.
- Mining – mining activities in the region may also create demand for anchor systems.
- Energy sector – this includes the construction and maintenance of power transmission infrastructure which drives the demand for cross plate anchors.
Frequently asked questions
This is an anchor used in the construction industry to anchor guy wires, fences and other structures to the ground. It is a strong and durable anchor that can withstand a wide range of loads in South America.
Cross plate anchors are suitable for a wide range of soil conditions including cohesive soils, loose soils, saturated soils and rocky soils.