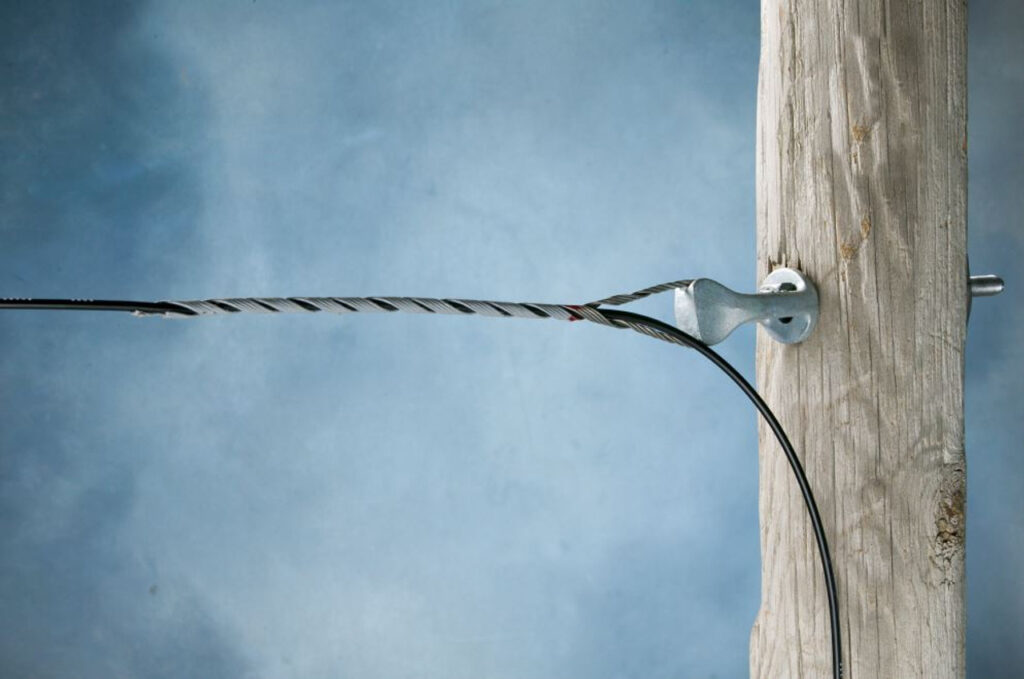

A service grip dead end is also known as a preformed dead end grip or a dead-end grip. It helps to terminate and anchor conductors on overhead transmission lines. It also provides a secure and permanent connection between the conductor and an anchoring structure. Dead end grip also has designs to withstand the tensile forces exerted by the conductor. This helps to ensure the conductor remains attached preventing it from slipping. A service grip dead end has helical rods designed to wrap around the conductor without causing damage. The wrapping creates a frictional grip that distributes the tensile forces along the length of the conductor. The dead end grips serve in terminating conductors, mid-span support and guy wires. Using service grip dead ends prevent hazards such as conductor slippage, sagging or breakage.
Accessories used with a service grip dead end
Service grip dead ends work with various accessories to ensure proper installation, stability and functionality. The accessories enhance the performance and safety of the dead ends and transmission lines. They also provide mechanical support, electrical insulation, vibration damping and grounding. The following are the common accessories used with service grip dead ends.

- Thimble eye – this is a metal loop that provides a smooth, rounded surface for connecting a shackle. It helps distribute the load and prevents grip damage.
- Shackles – these are U-shaped metal pieces used to connect the thimble eye of the service grip dead end to another hardware. They come with a removable pin for easy attachment and detachment. They may include anchor shackles or chain shackles.
- Insulators – these help in isolating the conductor from the support structure while supporting the dead end. These include use of suspension insulators and strain insulators.
- Eye bolts and eye nuts – these help to create a secure attachment points on poles or towers for connecting the dead ends. Bolts with a lop at one end anchor the dead end to a pole or structure. The nuts with a loop work with threaded rods to secure dead ends.
- Clevises – these are C-shaped connectors used to link the dead end to other components like insulators. They allow for rotational movement helping to relieve strain and prevent twisting.
- Guy grips – these are like service grip dead ends designed for guy wires. They provide extra structural support to poles and towers.
- Armor rods – these are helical rods placed around the conductor at points of stress. They protect the conductor from mechanical damage and stress concentrations.
- Preformed ties – these help to secure conductor to insulators to ensure they remain in place. They ensure the conductors remain in place even under mechanical stress or environmental conditions.
Conductor compatibility with service grip dead ends
It is crucial to consider conductor compatibility when selecting and installing the dead ends. The right match reduces mechanical stress and maintain electrical continuity. Consider the types of conductors and factors influencing compatibility. Service grip dead ends work with various conductors. This is including aluminum conductors, copper conductors and aluminum-clad steel conductors. The following are the factors influencing conductor compatibility with service grip dead ends.

- Conductor size – the service grip dead end must match the diameter of the conductor to ensure a secure fit. The cross-sectional area impacts the mechanical and electrical load capacity. Manufacturers provide specifications for the range of compatible diameters.
- Conductor material – different materials have varying tensile strengths and flexibility. They have designs to accommodate the differences to ensure a secure grip. It also helps prevent galvanic corrosion which occurs when different metals are in contact.
- Tension requirements – the dead ends must be able to withstand the greatest tension load that the conductor will experience. Proper tension helps control conductor sag, maintain clearances and reduces mechanical stress.
- Environmental conditions – conductors expand and contract with temperature changes. The dead ends must accommodate the variations without losing grip. Materials used in the conductor and dead end must resist environmental degradation.
Technical specifications for service grip dead ends
Technical specifications for service grip dead ends provide the necessary information to ensure proper selection. Consider the material properties, conductor compatibility, mechanical and electrical specifications. This ensures the dead end performs reliably and safely in your transmission. Additionally, referring to the technical specifications help to ensure they meet your requirements. The following are the technical specifications for service grip dead ends.
| Catalog Number | Diameter Range Min | Diameter Range Max | Units | Wt./Lbs. | Length (In.) | Color Code | Max. Neck Dia. (In.) |
| SG-11 | .169 | .198 | 300 | 24 | 11 | Blue | 2-3/8 |
| SG-12 | .199 | .224 | 300 | 27 | 12 | White | 2-3/8 |
| SG-13 | .225 | .257 | 300 | 29 | 13 | Orange | 2-3/8 |
| SG-14 | .258 | .289 | 200 | 27 | 14 | Black | 2-5/8 |
| SG-15 | .290 | .325 | 200 | 28 | 15 | Red | 2-5/8 |
| SG-17 | .326 | .360 | 200 | 31 | 17 | Green | 2-5/8 |
| SG-19 | .361 | .400 | 100 | 28 | 19 | Yellow | 2-7/8 |
- Material composition – the material of a service grip dead end is important for its performance and durability. The materials should be resistant to environmental factors such as corrosion.
- Conductor compatibility – ensure the dead ends match the conductor type and specifications. Compatible conductor types include AAC, AAAC, ACSR, solid copper and aluminum-clad steel.
- Mechanical properties – key mechanical properties ensure the dead end grip can handle the mechanical stresses of the application. Consider the rated tensile strength, ultimate tensile strength and breaking load.
- Dimensions – right dimensions ensure the proper fit and function of the dead end. Check the length of the dead end grip including any attachments or extensions. The diameter and weight of the dead end is also important for handling and installation.
- Performance testing – the specifications should include details about performance testing to ensure reliability. It should include the load testing and environmental testing results of the dead end grips.
Cost comparisons and considerations for the dead end grips
It is important to check both the cost and the performance characteristics of the dead end grip. The costs vary depending on several factors including material, type, size and application needs. Normal cost for service grip dead ends range between $20 – $150. This is depending on type, material, installation complexity and maintenance costs. Additionally, understanding these factors help in budgeting, selection, and optimizing the system costs. The following are the common factors influencing costs for service grip dead ends.
- Material costs – this may include the type of material and material quality. Galvanized steel is less expensive than other materials while aluminum and copper cost more. This is due to the high market value and they offer better corrosion resistance. High quality materials are more expensive due to enhanced properties.
- Manufacturing process – techniques like precision manufacturing increases costs due to higher precision and lower tolerances. Larger production batches reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Enhanced quality control measures and extensive testing for compliance with standards can increase manufacturing costs.
- Design and specifications – custom designs tailored for specific applications are costly due to extra designs. Dead ends are also designed to handle higher tensile loads or specific environmental conditions.
- Conductor compatibility – dead ends have designs to fit a wide range of conductor types and sizes. They are also compatible with less common conductors which may incur higher costs due to lower production volumes.
- Market factors – prices for raw materials like steel, aluminum and copper vary based on global market conditions. Supply chains can also lead to increased raw material costs and higher product prices.
- Distribution and logistics – costs for dead end grips cat depending on the size, weight and shipping distance of the dead ends. Shorter lead times may incur extra costs die to expedited manufacturing and shipping.
Troubleshooting service grip dead ends
Troubleshooting helps to maintain the integrity and reliability of overhead transmission systems. Problems with the service grip dead ends can lead to mechanical failure, increased maintenance costs and safety hazards. The following is a guide to troubleshooting problems associated with service grip dead ends.
- Visual inspection for physical damage – check for signs of cracks, corrosion, rust, wear and abrasion. Replace any dead ends showing significant damage to prevent failure.
- Checking for proper installation – check for incorrect tensioning, improper alignment and incomplete installation. Reinstall the dead end grips according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Monitoring for electrical continuity – ensure proper electrical continuity by checking for increased electrical resistance. Clean and tighten any corroded or loose connections.
- Identify mechanical stress and fatigue – check for signs of mechanical stress like discoloration, micro-cracks and conductor damage. Adjust the tension to reduce stress and distribute the load.
- Ensure proper compatibility – incorrect sizing and material incompatibility may lead to several issues. Ensure the dead end matches the conductor’s specifications for size and material.
Frequently asked questions
A service grip dead end is compatible with a variety of conductor types. These include AAC, AAAC, ACSR, Solid copper, Stranded copper, and aluminum-clad steel.
The main factors that influence the price of service grip dead ends include material costs, manufacturing process, design specifications and conductor compatibility. It also includes market factors, installation and maintenance, distribution and logistics.