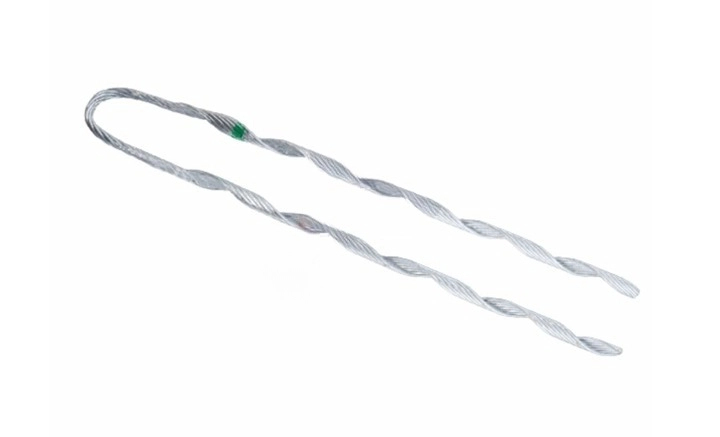

A slack span dead end is a specific type of conductor arrangement and support. Its primary goal is to offer a secure termination point for the conductor. It accomplishes this while allowing for some flexibility and movement in the conductor. Slack span dead ends serve where the line needs to make an abrupt turn at the end-of-line poles. The conductor anchors at the slack span dead end using moveable hardware. These hardware components include clamps, insulators, and other fittings. A “slack span” is a small length of conductor that is not under significant tension. A dead end is a place in the transmission line where the conductor is firmly anchored.
The Importance of Using a Slack Span Dead End
Using a slack span dead end improves the system’s reliability, safety, and maintenance. It reduces tension on the support structures on either side of the river, allowing for a safer and more stable crossing. The following are the benefits of a slack span dead end.
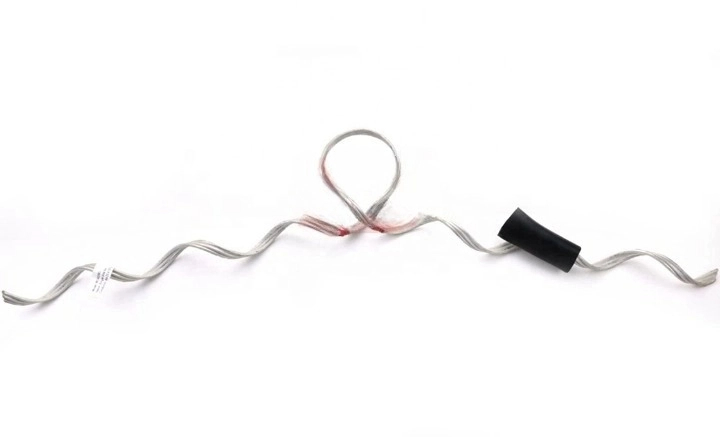

- Enhanced flexibility and adaptability – the dead ends provide flexibility to absorb movements caused by wind or thermal expansion. They work in areas where the transmission line needs to change direction and ensure the conductor can adapt to the new path without stress.
- Improved maintenance and inspection – maintenance crews can access the conductors for repairs, adjustments or replacements.
- Reduced tension on structures – the slack span dead ends reduce the tension exerted on supporting structures. This helps to reduce the risk of structural failure and preserves the integrity of poles.
- Enhanced safety and stability – reduced tension reduces the likelihood of conductor breakage. The design can help reduce the risk of galloping in windy conditions.
- Cost efficiency – the slack span dead ends reduce the load on structures and reduce wear on components. This can lead to lower ling-term maintenance costs.
- Ease of integration with existing systems – the dead ends ease the integration of new sections of transmission lines. This allows for smooth transition between different types of structures or conductor configurations.
- Compatibility with various terrain – slack spans can manage the differences in uneven terrain. This is to provide a practical solution for line installation. They offer the flexibility to accommodate various line layouts. This makes it easier to design and implement transmission lines.
- Mitigation of mechanical loads – slack span dead ends distribute mechanical loads along the line. This is to reduce the impact of sudden load changes. They act as buffers against dynamic forces like wind and ice to help maintain the integrity of the line.
Fittings used with a slack span dead end
Slack span dead ends need a variety of accessories to ensure proper operation and system integrity. The accessories make it easier to secure anchor the conductors while also providing flexibility and protection. Also, integrating these accessories allows engineers to verify that the slack span dead ends provide a secure, adaptable, and dependable source of support. The following are the accessories for slack span dead ends.
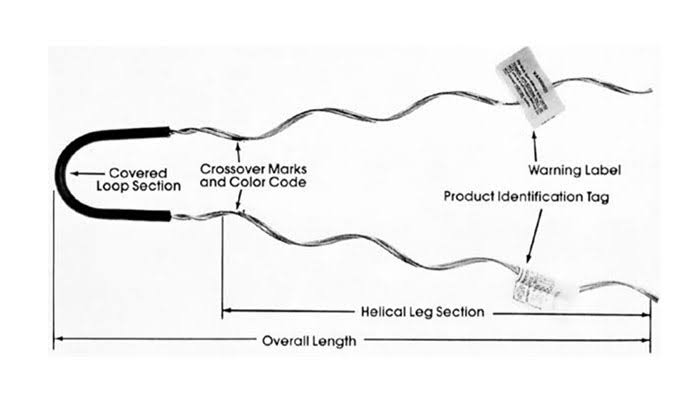
- Insulators – these help to electrically isolate the conductor from the support structure. They include pin insulators, suspension insulators and strain insulators. These insulators prevent electrical conduction to the support structure and provide insulation.
- Guy wires and guy grips – these provide extra support and stability to slack span dead ends. They anchor the structure to the ground to ensure a firm attachment.
- Tensioning devices – these help to apply and maintain the correct tension in the conductor. Turnbuckles and tensioning devices allow for precise adjustment and apply the necessary tension.
- Dead end clamps – these aid in anchoring the conductors at the end of the slack span. Common types used include bolted dead end clamps, compression dead end clamps and wedge type dead end clamps.
- Preformed armor rods – their purpose is to protect the conductor from abrasion and mechanical damage at points of stress. They have a helical shape to wrap around the conductor to distribute stress and provide a protective layer.
- Vibration dampers – these mitigate vibrations caused by wind or other factors that can lead to fatigue and damage over time. Stockbridge dampers dissipates vibrational energy while spiral dampers reduce vibrational amplitude.
- Spacer and spacer dampers – they maintain the separation between many conductors in a bundle. It also prevents clashing and maintaining electrical performance.
Slack deads end for ADSS cables
Slack span dead ends for ADSS cables come with special qualities to meet the cables’ unique requirements. The dead ends ensure that the cables maintain mechanical stability and endurance in a variety of environmental situations. Additionally, the design qualities ensure that the ADSS cables are properly supported and protected from environmental and mechanical pressures. The ADSS cable’s slack span dead ends have the following features.
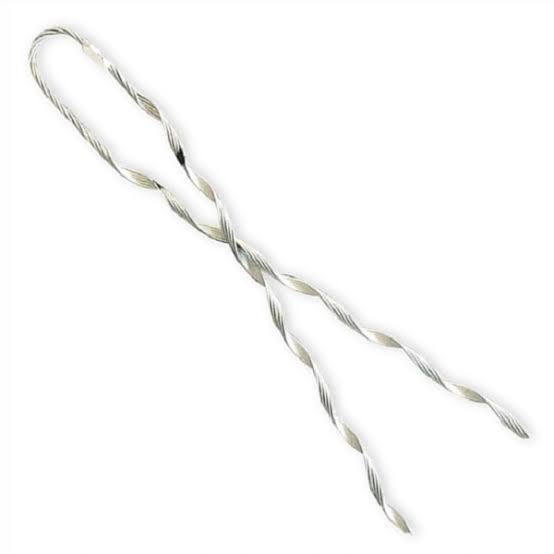

- Secure and reliable anchorage – slack span dead ends provide a secure anchorage for the cable without damaging the fibers inside. The anchoring system has designs to avoid causing any mechanical damage to the cables outer sheath.
- Electrical insulation – the dead end components are from non-conductive materials. These materials prevent electrical interference since ADSS cables are all dielectric.
- Flexibility and low tension – the dead ends have designs to maintain a lower tension in the ADSS cable compared to regular spans. The reduced tension allows for slight movements and prevents excessive stress on the cable.
- Vibration and motion resistance – the dead ends incorporate vibration damping accessories. They are to mitigate the effects of wind-induced vibrations. The design accommodates movements due to the environmental factors.
- Environmental durability – the dead ends are from materials that are resistant to environmental factors. These include UV radiation, extreme temperatures, moisture and chemical exposure.
- Compatibility with ADSS cable – the dead ends have designs to match the physical and mechanical characteristics of ADSS cables.
- Ease of installation and maintenance – slack span dead ends have designs for straightforward installation. Their flexible design reduces the need for frequent maintenance and any repairs.
- Mechanical strength and load capacity – the dead ends are able to support the weight and tension of the ADSS cables. The dead ends can absorb and dissipate mechanical shocks to protect the cable.
Slack span deads end for OPGW cables
Slack span for OPGW cables is a significant consideration when designing and installing overhead transmission lines. OPGW cables combine the roles of grounding and communication. This works by combining optical fibers onto a conductive metal thread. Additionally, dead ends assure the safety, durability, and efficacy of OPGW cable installations. The following are the features of slack span dead ends used with OPGW cables.

- Strong and reliable anchorage – dead ends provide a secure anchorage for the OPGW cable using various components. The anchoring mechanisms have designs to avoid causing any physical damage to the cable’s conductive components.
- Electrical insulation and conductivity – OPGW cables serve as both a grounding conductor and a communication medium. They help maintain the cable’s grounding function while ensuring the optical fibers are well protected.
- Compatibility with OPGW cable design – the dead ends are able to meet specific physical and mechanical characteristics of OPGW cables. They ensure the cables are not bent beyond a specified maximum.
- Reduced mechanical tension – slack span dead ends have designs to maintain a lower tension in the OPGW cable. The design allows them to distribute mechanical stress along the cable.
- Environmental resistance – components for slack span dead ends are from materials that can withstand environmental factors. They are also resistant to corrosion to prevent degradation.
Evaluating slack dead ends
Testing guarantees the dependability and safety of overhead transmission systems. Proper testing guarantees that dead ends can tolerate environmental stressors, mechanical loads, and electrical conditions without failing. Also, the tests confirm that the dead ends provide solid anchorage, preserve cable integrity, and contribute to reliability. The following are some popular tests for slack span dead ends.
- Vibration testing – this test is to assess the dead ends ability to dampen and withstand vibrations.
- Environmental testing – this is to check the performance of the dead end under various environmental conditions. This is including temperature extremes, humidity, UV exposure and corrosion.
- Tensile load tests – this is to verify the mechanical strength and lad bearing capacity of the slack span dead end.
- Electrical testing for OPGW – this test is to ensure the slack span dead end for OPGW cables can handle electrical loads ad provide grounding.
- Mechanical fatigue testing – this is to simulate long-term mechanical stress and check the dead ends durability over time.
Frequently asked questions
A slack span dead end is a device used to anchor and secure cables such as ADSS or OPGW at points where the cable is under lower tension. It distributes stress and accommodates slight movements protecting the cable from mechanical damage.
This includes matching the dead end components to the cable’s diameter, weight and mechanical qualities. It also includes ensuring that the dead end does not exceed the least bending radius.
They use vibration damping accessories which mitigate the effects of wind-induced vibrations and protect the cable from fatigue and damage.