
A service grip dead end is a component used to secure and support the conductors that carry electrical power. It helps prevent the flow of electricity in the event of a line break or other fault. It is also known as a dead-end grip or suspension grip. The hardware installs at the ends of the lines or at points where the conductor needs anchor. They are from high-quality materials to ensure the secure and long-lasting support of overhead conductors in Southeast Asian networks. Common types include wedge-type, socket-type, automatic, compression, grip clamps and swivel dead ends. They find use in applications such as transmission and distribution lines, telecommunications and aerial cables among others.
Key features of service grip dead end
The service grip dead end has various features that make them effective in securing and supporting overhead conductors. The help them provide secure support, tension control and durability to ensure safe and reliable operations. The following are the common features of the service grip dead ends.
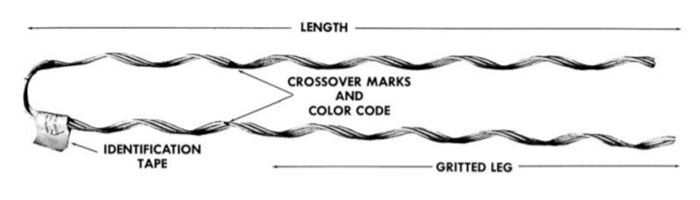
- Conductor compatibility – the hardware is able to accommodate a range of conductor sizes. This allows flexibility in various applications.
- High-strength materials – they are also from high-strength materials. These materials include aluminum or other alloys. This helps them to withstand mechanical stresses and environmental conditions.
- Secure grip – it also provides a secure and reliable hold on the conductor with grips such as wedges, sockets or clamps.
- Tension adjustment – this allows the line workers to fine-tune the tension in the conductor. This is to ensure it remains properly tensioned to meet safety and operational requirements.
- Durability -they can withstand harsh weather environmental conditions. These conditions include UV radiation, extreme temperatures and corrosive elements.
- Corrosion resistance – the hardware has coatings that allow them to work in outdoor applications.
Selection and installation of service grip dead end
The selected service grip dead end should ensure the safe and reliable operation of overhead conductors. This may include considering several factors to ensure the best selection. These factors include conductor size, application, load requirements, installation method, cost and environmental conditions. The installation process should ensure the secure and reliable support of overhead conductors. The following is a basic installation guide for the service grip dead end.
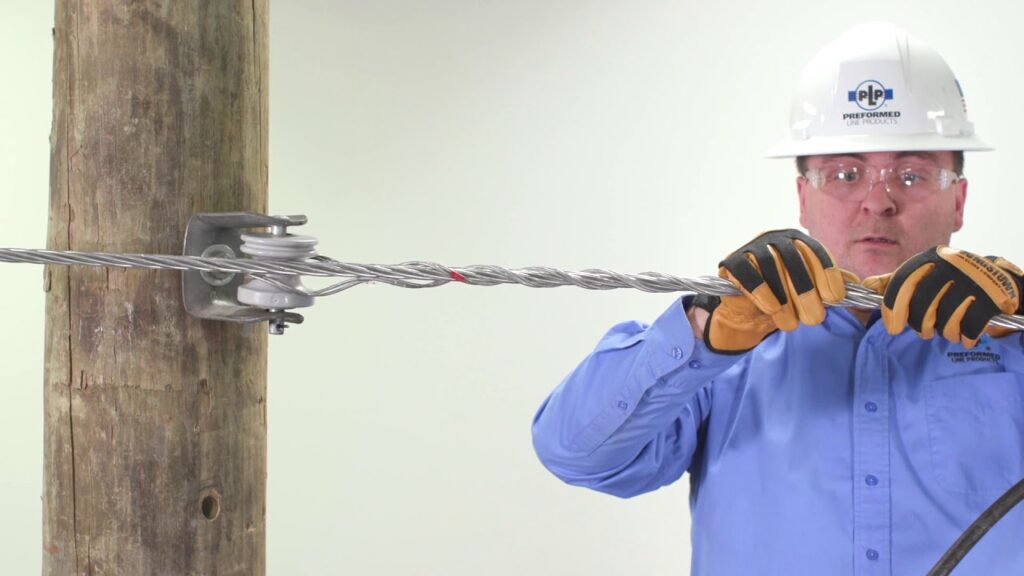

- Safety precautions – ensure all safety precautions are in place. This is including the use of personal protective equipment.
- Conductor preparation – ensure the conductor is clean and free or debris or contamination. Replace any worn or damaged conductors before installation.
- Selection – choose the service grip dead end that matches the size of the conductor and the specific requirements of your application.
- Attachment – place the grip over the conductor and ensure it is properly aligned and centered. Ensure to follow all the manufacturers guidelines for attachment.
- Tightening – use the suitable tools to securely tighten the grip onto the conductor.
- Inspection – inspect the grip and the conductor to ensure the proper security and alignment.
- Tensioning – use the suitable tensioning device to achieve the desired tension level. Ensure all personnel are clear of the tensioning area to avoid accidents.
- Inspection – conduct a final inspection to ensure the installation meets safety and quality standards.
- Documentation – maintain detailed records of the installation. This is including dates, location, grip type, conductor size and other relevant details.
Maintenance and inspection of service grip dead ends
Conduct regular maintenance and inspection of the dead ends. This is to ensure their continued performance and safety. This also helps to identify and address potential issues before they become safety hazards or lead to system failure. These practices help ensure the reliability and longevity of the overhead conductor and cable systems. The following is a basic guide to the maintenance and inspection of service grip dead ends.

- Create a maintenance schedule including routine inspections of all dead-end grips in the system. The frequency depends on environmental conditions, conductor load and manufacturer recommendations.
- Visually examine each grip for signs of wear, damage or corrosion and look for loose fasteners or cracks.
- Check the tightness of fasteners, bolts and nuts and use a torque wrench to ensure the hardware is properly tightened.
- Clean the grips of dirt, dust or contaminants using a suitable cleaning method. Use a clean, dry cloth and do not introduce additional contaminants during cleaning.
- Apply lubrication to moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Replace any grips with signs of wore, damage or corrosion with genuine replacement parts.
- Check the tension to ensure it is within the recommended range.
- Ensure the grips remain compliant with relevant industry standards and regulations for safety of the installation.
- Consider the environmental conditions to ensure the grips remain resistant to corrosion, UV degradation and other environmental factors.
- Maintain detailed records of your inspections including dates, locations and any findings or maintenance taken.
Comparative analysis of service grip dead end
A comparative analysis involves assessing different types of grips and manufacturers. It helps identify the service grip dead ends that best align with the specific needs and challenges of the installation area. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with experts in the region to make informed decisions. The following are the common factors to include in a comparative analysis in Southeast Asia.
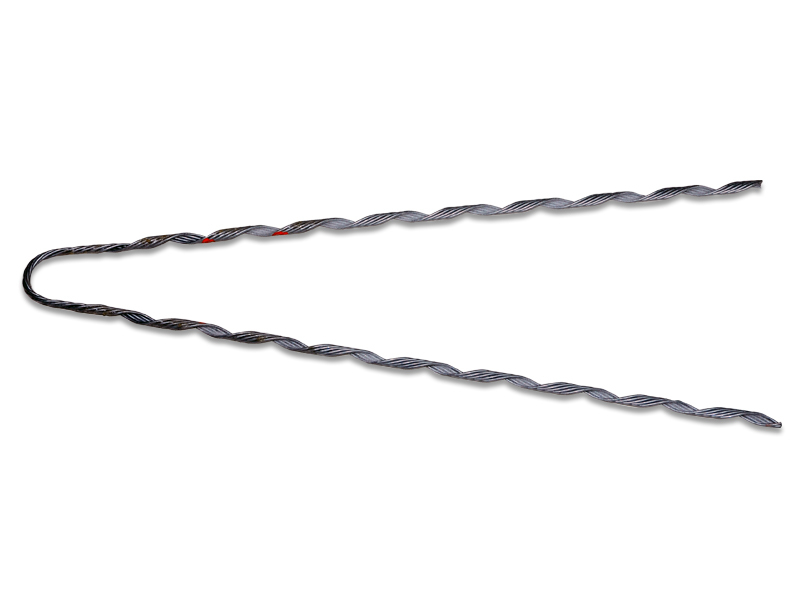

- Conductor size compatibility – compare the range of conductor sizes to accommodate and the variation in conductor sizes.
- Environmental resilience – evaluate the grip’s resistance to the region’s tropical climate, high humidity and exposure to UV radiation.
- Load capacity – compare the load bearing capacity of each different grip models to ensure they can handle the expected loads.
- Tensioning mechanisms – compare the tension adjustment mechanisms. This helps to ensure they meet the tensioning requirements.
- Material quality – assess the quality and durability of materials used in the grip manufacture.
- Manufacturer reputation – the manufacturer should have a track record of providing reliable grips.
- Cost considerations – assess the cost effectiveness of each grip type. Consider both upfront cost and long-term maintenance expenses.
- Longevity and warranty – consider the expected lifespan of the grips and whether they have warranties.
Certifications and standards in Southeast Asia
The certifications and standards for the service grip dead ends in Southeast Asia vary depending on the specific country. There are also other international and regional standards and certifications adopted in the region. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with local authorities for guidance on the applicable standards and certifications to meet. The following are the common standards and certifications in Southeast Asian market.
- IEC standards – this standard specifies requirements and tests for dead-end fittings.
- ASTM international standards – This includes standards for test methods.
- Local and national standards – each country in Southeast Asia has their own specific standards and regulations. Some countries adopt or reference the international standards for electrical equipment.
- ISO certification – these are for manufacturers to indicate the quality of their products.
- CE marking – CE marking demonstrate compliance with European Union safety and environmental standards.
- Manufacturer’s certifications – manufacturers may have their own certifications or product documentation. This is to demonstrate compliance with relevant standards and specifications.
Regional markets for service grip dead ends in Southeast Asia
There are various factors that influence the regional market for service grip dead ends in Southeast Asia. The demand for service grip dead ends is mainly driven by the need for secure and reliable support of overhead conductors. There are various factors that may lead to the increased demand for the grips which may lead to market changes. The following are the key factors that shape the regional market for service grip dead ends in Southeast Asia.

- Infrastructure development – the ongoing projects in power generation, distribution and transportation increase the demand for the dead ends.
- Telecommunication expansion – the growth of these networks contributes to the demand for grips that securely hold and protect the cables.
- Transportation and railways – the expansion of projects such as high-speed rail projects require grips. They help to support catenary wires and ensure safe and reliable operation.
- Energy efficiency – increasing energy efficiency and grid reliability in the region promotes the use of high-quality grip dead end. They also help reduce energy losses through sag control and proper tensioning of conductors.
- Local production – local manufacturers produce service grip dead ends to meet the regional demand. This helps them tailor the products to suit local requirements.
- Environmental factors – the tropical climate, high humidity and exposure to harsh weather conditions necessitate the use of service grip dead ends.