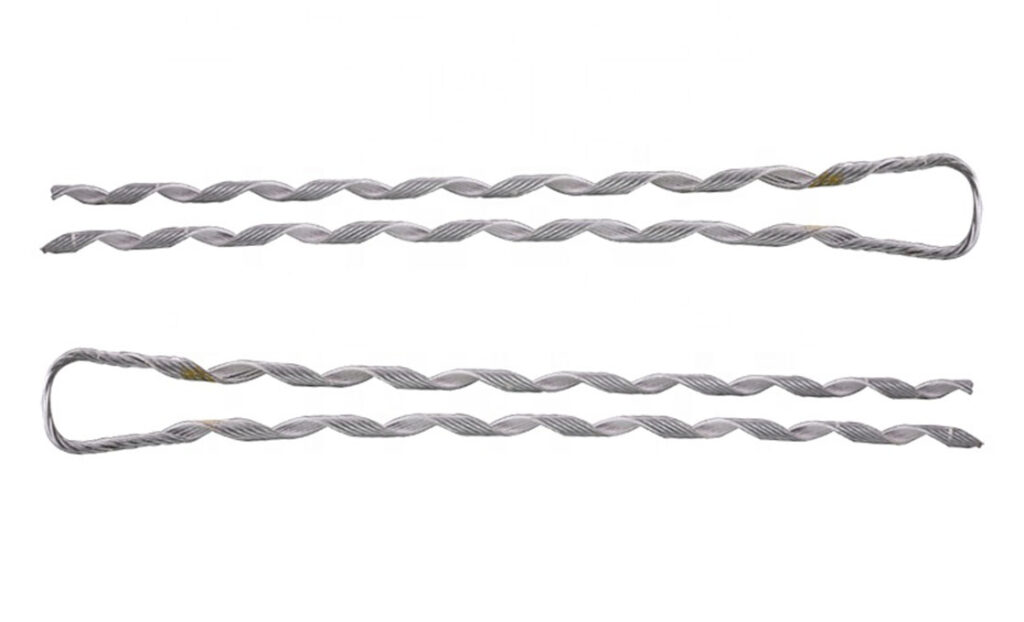

A preformed tension clamp is a type of clamp used on the power lines. It helps to provide mechanical support and tensioning of conductors. It’s design help find use in overhead power transmission and distribution systems. They secure and support the conductor in a tensioned position. The tension clamps are from high-strength materials such as aluminum alloy or steel. It has specific contours and shapes to accommodate the conductor and provide secure grip. The design allows for the adjustment and control of the tension applied to the conductor. The clamps also help prevent excessive sagging and vibration or movement of the conductor.
Components of the preformed tension clamp
The specific components and their arrangement vary between different manufacturers and design. The components work together to secure and support the conductor on the power lines. The design and components may also vary depending on the manufacturer and application. The following are the components of the preformed tension clamps.
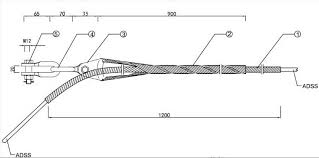
- Gripping elements – These are the features that directly engage with conductor to provide a secure grip. Gripping elements can be in the form of serrated jaws, wedges or other structures. They help to hold the conductor firmly in place.
- Clamp body – Clamp body serves as the main structure that houses the gripping elements. It is from durable and corrosion resistant materials like aluminum alloy or steel.
- Fastening fittings – Preformed tension clamps work with bolts and nuts to secure the clamp body.
- Tensioning device – The device allows for the adjustment and control of the tension applied to the conductor. It includes components like a threaded rod, turnbuckle and other tensioning elements. These helps to facilitate the desired tensioning of the conductor.
- Spacer plates – Spacer plates provide separation and insulation between the clamp body and the conductor. They prevent electrical contact or galvanic corrosion between the clamp and the conductor.
- Coatings – Protective coatings enhance durability and resistance to corrosion. This helps to prolong the lifespan of the clamp.
Types of the preformed tension clamps
The types of preformed tension clamps vary in design, materials and specific applications. Choosing the preformed tension clamp depends on some factors. They include conductor size, tension requirements, and specific installation requirements. The different designs and specifications allow them to be applicable in various applications. The following are the common types of preformed tension clamps.
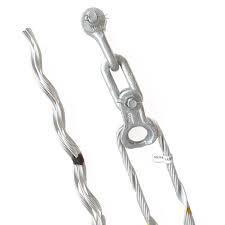
- Dead-end clamps – Dead-end clamps are also used to secure the conductor at the termination points. They install where the conductor ends or where it attaches to insulators or poles.
- Suspension clamps – Suspension clamps support the weight of the conductors in transmission and distribution lines. They install at the suspension points along the power line to maintain the desired tension. This also helps to prevent excessive sagging.
- Mid-span clamps – The clamps provide extra support and tension control at the intermediate points along long spans of power lines. They reduce excessive sagging and ensure the proper tension distribution along the conductor.
- Strain clamps – The strain clamps provide tension and anchor the conductor. They also absorb the mechanical forces generated by the tension in the conductor and maintain its position.
- Guy wire clamps – Guy wire clamps have a design that secure the guy wires used to support power line structure like poles. They provide tension and stability to the guy wires. This ensures proper alignment and support for the power line infrastructure.
- Armor rod clamps – These are also known as vibration dampers used to reduce the vibration and oscillation of conductors. The vibration is from wind or other dynamic forces.
Applications of preformed tension clamps
The specific application of preformed tension clamps varies depending on the type of power line, voltage level and conductor size. Industry professionals can provide guidance on use of the clamps in specific applications. The following are the applications of the preformed tension clamps.
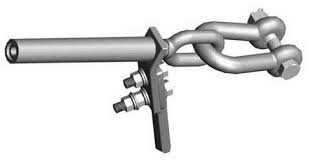
- Guy wires – Tension clamps ensure proper tensioning of the guy wires and structural stability. They also prevent excessive movement or swaying.
- Overhead transmission lines – Preformed tension clamps help to support and tension the conductors on the transmission lines.
- Railway electrification – Preformed tension clamps help to secure and tension the overhead or contact wires. They provide the necessary support and tension to ensure continuous and reliable power supply to electric trains.
- Substation installations – Preformed tension clamps work in substation installations to support and tension the conductors. They also maintain proper tension in the cables or busbars.
- Communication lines – The clamps also work in installations such as fiber optic cables or telephone lines. They assist in securing and tensioning the communication cables. It also ensures reliable transmission of signals over long distances.
- Distribution lines – The clamps deliver electricity to residential, commercial and industrial areas. This provides the necessary tension for efficient power distribution
Installation of the preformed tension clamps
Some of the manufacturers in the market offer installation instructions for the clamps. They may include additional steps or considerations specific to the particular clamp design. It is essential to ensure a safe and reliable installation of preformed tension clamps on power lines. Below is a step-by-step installation process of the preformed tension clamps.
- Site survey – Conduct a site survey to assess the power line which determine the appropriate locations for the tension clamps. They also ensure that all the necessary tools and equipment are available.
- Prepare the conductor – Ensure the conductor is clean and free from any debris or contaminants that could affect the grip of the tension clamp.
- Position the tension clamp – Position the tension clamp at the desired location on the conductor. This will depend on the application and design requirements.
- Align the gripping elements – Align the gripping elements of the tension clamp with the conductor. Ensure they position correctly and in contact with the conductor’s surface.
- Apply tension – Apply the needed tension to the conductor by adjusting the tensioning device or mechanism if provided.
- Secure the clamp – Secure the tension clamp to the conductor using the provided bolts, nuts and others to ensure the clamp is tight.
- Inspection – Conduct a visual inspection of the installed tension clamp to ensure that it is properly aligned, securely fastened and free from defects or damages.
- Repeat for additional clamps – This includes areas where multiple tensions are necessary along the power line. Repeat the above steps for each clamp to ensure proper spacing and tension distribution.
Choosing the best clamp for power line applications
It is advisable to consult with electrical engineers with experience in power line installations. They provide specific guidance based on the requirements and conditions of your power line project. There are various factors to consider as detailed below.

- Consider the specific application and line design requirements. Determine whether the tension clamp is necessary for suspension points, dead ends and mid spans.
- Different clamps are for specific conductor types and sizes. Consider this and ensure they are compatible with the conductor you are working with.
- Assess the material of the tension clamp to consider the corrosion resistance properties. This is especially when working in environments with harsh conditions.
- Evaluate the tensioning and load capacity of the tension clamp. Consider the required tensioning type for the conductor. This helps to verify that the clamp matches or exceeds the expected loads and stresses.
- Consider the relevant industry standards, regulations and codes of using the preformed tension clamps. This is important for safety, reliability and compatibility with the power grid infrastructure.
- This checks on quality, reliability and customer support for each manufacturer. Consider the availability of technical documentation, installation guidelines and access to manufacturer support.
- Consider the cost effectiveness of the tension clamp to ensure quality and performance. Compare prices and features from different manufacturers.