
Shackle insulator is a type of insulator used on low voltage transmission lines. Their design helps to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support for the conductor. The shackle insulators are mainly from materials like porcelain, glass or polymer. The materials help in resisting different environmental conditions. Shackle insulators install at a suspended manner connecting the conductor to the support structures. The main purpose of the shackle insulator is to maintain a safe distance between the energized conductor and the grounded structure. This helps to prevent electrical current from flowing to the unwanted areas in the power lines. Shackle insulators are also designed to withstand high voltage and mechanical stresses like wind loads and conductor tensions.
Components of a shackle insulator
Shackle insulator consists of various components working together to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support. The components of the insulators vary depending on the design and construction of the insulator. They also ensure safe and reliable transmission of electricity over long distances. The various components of the shackle insulator are as discussed below.
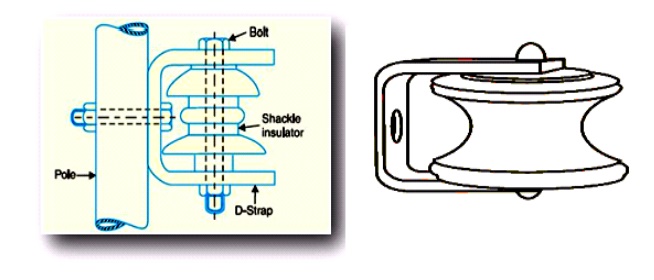
- Insulating housing – this is the main body of the shackle insulator made of porcelain or polymer materials. It provides the insulation between the conductor and the support structure. It helps provide high electrical resistance and withstand the voltage stress applied during transmission line operation.
- Core rod – this is a central structural component of the shackle insulator usually made of metal or composite material. It is securely attached to both ends of the insulating housing and supports the load of the conductor.
- End fittings – these are connectors that secure the insulating housing and core rod to the conductor and the supporting structure. They provide sturdy and reliable connection since they have a threaded or bolted connections. This helps to facilitate installations and maintenance.
- Sealing material – sealing material help to ensure the stability and integrity of the shackle insulator. It fills any gaps between the insulating housing, core rod and end fittings to prevent moisture from entering the insulator.
- Fittings – shackle insulator uses various fastening fittings like bolts, nuts and washers. These helps to secure and assemble the different parts of the shackle insulator.
Types of shackle insulators
When it comes to selecting shackle insulators, there are various types of them to choose from. The types are mainly categorized according to the materials they are from. It also depends on the intended use of the insulator and the type of application to work in. Other factors include the voltage level, mechanical load and environmental conditions. Below are the common types of the shackle insulators.

- Hybrid shackle insulator – hybrid shackle insulators have a porcelain core and end fittings. They also have an insulating housing made of composite material. They offer balance between the mechanical strength of porcelain and the pollution resistance of composites.
- Porcelain shackle insulator – these are from high-strength porcelain materials which provides excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength. They offer durability, resistance to pollution and ability to withstand high voltages.
- Insulated shackle insulator – insulated shackle insulators feature a metal rod covered with an insulating sheath. This design prevents flashovers and enhances the electrical insulation properties.
- Composite shackle insulators – these manufacture using fiberglass-reinforced polymer materials. They offer benefits like lighter weight, high mechanical strength and resistance to pollution and wreckage.
- Polymer shackle insulators – polymer insulators provide good electrical insulation, light weight construction and resistance to pollution. They are work in low to medium voltage transmission lines.
Applications of the shackle insulators
Shackle insulators are essential components as they provide insulation and mechanical integrity. This ensures reliable and efficient transmission of electrical power. Discussed below are the various applications of the insulators.

- Shackle insulators work in distribution lines to deliver electrical power from transmission lines to consumers.
- They provide electrical insulation and support to the conductors on the electrical transmission lines.
- They work in railway electrification systems where overhead catenary wires help to supply power to trains.
- Shackle insulators help to withstand the high electrical stresses and voltages encountered in these applications. They also ensure the safe and reliable transmission of power from transmission lines to consumer.
- Shackle insulators play a vital role in high-voltage direct current transmission systems used for long distance power transmission.
- They help insulate and support the conductors within the substation. This ensures the safe and efficient flow of electricity.
Installation of shackle insulator
The installation process of the shackle insulators varies depending on various factors. These includes the specific requirement, design, material and manufacturer of the insulator. Additionally, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek for assistance from experts to ensure proper and safe installation. The basic installation process is as discussed below.
- Ensure that you adhere to all necessary safety precautions. These includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment to ensure a safe working environment.
- Gather all the required tolls and equipment for the installation. These may include insulators, fasteners, hardware to ensure they are in good condition.
- Identify the location on the transmission line where the insulator needs to install. This also determines the spacing and height based on the line design and electrical specifications.
- Install the insulator following the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the insulator aligns and attaches securely.
- Ensure all connections are tight and secured. This is by using the appropriate tools to tighten bolts, nuts and clamps according to the specified torque values.
- Use maintenance loops or tie-wires in areas with high wind loads for additional security.
- Conduct a visual inspection to ensure that the insulator is properly installed, aligned and secured. You should check for any signs of damage, misalignment or loose connections.
Choosing the best shackle insulator in the market
The market is full of insulators with different design, shapes and sizes. These are from different manufacturers and suppliers in the market. Select the best shackle insulator based on the type of application and the specific requirements needed for your project. Below are the various factors to consider when selecting the best shackle insulator.

- Determine the voltage level of the transmission line or system where the insulator will install. The voltage level should match with the system requirements.
- Evaluate the mechanical load that the insulator will experience like tension, compression, wind loads and conductor weight.
- Consider the environmental conditions in which the insulator will work on. Check the pollution, salt spray, temperature variations and UV exposure. These conditions can impact the insulator performance.
- Check the material used to make the insulator which have different advantages and considerations.
- Select an insulator with excellent pollution performance. This is to ensure reliable operation in polluted environments.
- Consider the maintenance requirements of the insulator. Some insulators may require frequent cleaning or inspections.
- Ensure the selected insulator meets the relevant industry standards and regulations. These include ANSI, IEC of other national standards.
- Consider the reputation and track record of the manufacturer or supplier. They should have a record for producing high quality and reliable insulator.