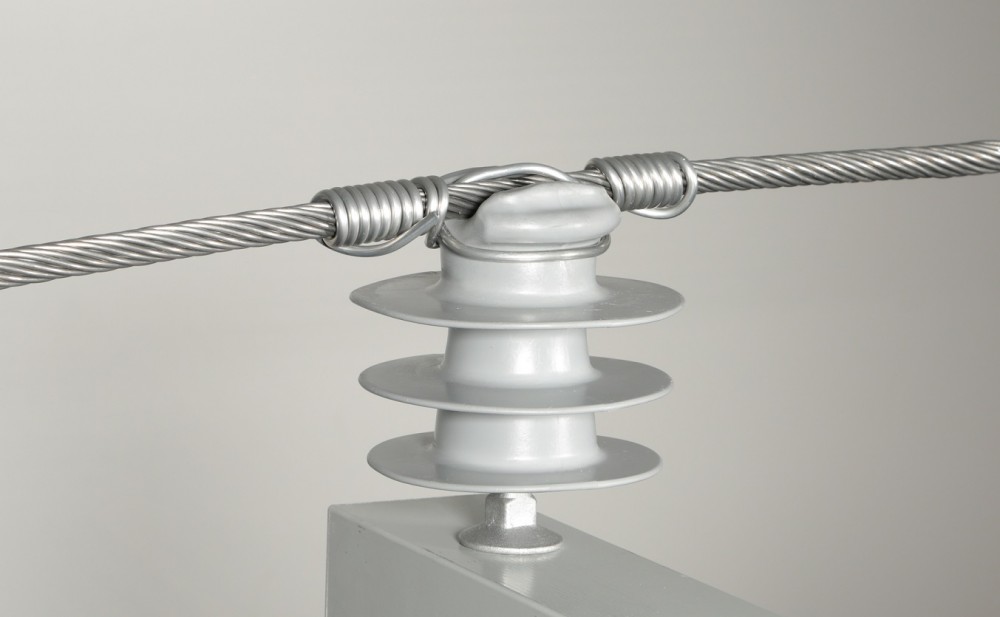

A line guard is a protective device used to maintain a safe distance between conductors and nearby objects. It helps to prevent unintended contact which could lead to electrical faults. A line guard is also from insulating materials like fiberglass and other non-conductive materials. It creates a physical barrier between conductors and other structures like trees and buildings. Thus, a line guard mainly helps to reduce the risk of short circuits. It also helps reduce electrical arcing caused by objects coming into contact with lines. It is from durable materials that help to ensure longevity and resistance to environmental factors. Line guards revolutionize electrical safety in South American countries. This is to provide a protective shield for transmission lines. Examples include spacer dampers, bird flight diverters and spacer cable systems. They find use in applications such as electrical safety, wildlife protection and preventing galloping.
Key features of line guard
Line guards have a wide range of features that help to contribute to safety and reliability of the electrical grid. They also help make them a popular choice in the electrical industry. These features include:
- Insulating properties – this is one of the primary purposes of the for the line guard. Line guards have high electrical insulating properties to prevent unintended contact. This also helps reduce the risk of electrical faults.
- Corrosion resistance – line guards have high corrosion resistance to increase the durability of the equipment. It protects them from areas with high humidity or corrosive substances.
- Vibration damping capability – they also have vibration damping capabilities to stabilize conductors, prevent galloping and sway.
- Corona control – controlling the corona effect includes the ability to reduce radio interference.
- Visibility enhancement – this includes features that enhance visibility of transmission lines to wildlife. This mainly helps to prevent bird collisions and reduce impact on ecosystems.
- Ease of installation – they also have designs that facilitate ease of installation on existing lines. This also helps to ensure the utilities implement safety measures without disruptions.
- Material durability – they are from durable materials like fiberglass, polymers or other non-conductive substances.
Selection and maintenance of line guard
Proper selection of the line guard helps to ensure the safety and reliability of power transmission systems. It includes considering factors such as voltage ratings, material compatibility, insulating properties, weather resistance, ease of installation and cost effectiveness. The installation process requires precision and adherence to safety guidelines. The following is a general installation process of the line guards on transmission lines.

- Site assessment – conduct a site inspection to identify the specific conditions and requirements of the transmission lines. Consider factors such as voltage levels, environmental conditions and the type of line guard needed.
- Equipment preparation – ensure you have all the necessary tools and equipment for the installation. These include safety gear, insulating tools and specialized equipment.
- Transmission line preparation – de-energize the transmission lines following established safety procedures. Secure permits and approvals for working the lines and ensure tagout to ensure the safety.
- Line guard installation – this involves fitting insulating line guards onto the conductors, attaching bird flight diverters and securing vibration dampers on suitable locations.
- Alignment and clearance – ensure the line guards have proper alignment to provide the necessary clearance between conductors and nearby objects.
- Secure line guards in place – ensure all the connections are tight and securely attached to the transmission lines to withstand environmental conditions.
- Inspections and tests – conduct a thorough inspection of the installed line guards to check for any defects or issues.
- Energize the transmission lines – once the line guards install. Follow established procedures to safely energize the transmission lines.
- Documentation – maintain detailed records of the installation process. This is including any tests conducted, adjustments made and relevant safety documentation.
Maintenance and inspection of line guards
Periodic inspection and maintenance of line guards help to ensure the continued performance and reliability of overhead transmission lines. The diverse environmental conditions in South America influence the frequency of the activity. Additionally, it helps to identify and address potential issues that may cause failures and accidents. The following is a basic guide for maintenance and inspection of line guards.

- Conduct routine visual inspections to check for any visible signs of damage, wear or corrosion on the line guards. Check for signs of cracks, loose fittings and any other issues.
- Inspect the bird diverters for proper alignment and visibility to enhance bird deterrence and prevent collisions.
- Inspect spacer dampers and vibration dampers for signs of wear or damage. check their connections and ensure they are securely in place. This is to prevent conductor galloping and sway during windy conditions.
- Inspect any available corona rings for signs of wear or damage. Verify they are effectively controlling the corona effect and reduce radio interference.
- Perform electrical tests on insulating line guards to verify their insulating properties. This is to ensure they continue to provide effective protection against unintended contact between conductors.
- Regularly clean the line guards to remove dirt, dust or other contaminants accumulated over time.
- Check and tighten fasteners and fittings as part of scheduled maintenance to ensure all connections are secure.
- Consider applying protective coatings or using corrosion-resistant materials to extend the life of the line guards.
- Maintain detailed records of all inspections and maintenance activities. Document any replacements made, repairs made and conditions of each line guard.
Comparative analysis of line guard in South America
Conducting a comparative analysis involves evaluating and assessing different types of line guards based on various factors. It involves analysing the different types, designs and brands. It also includes comparing the materials which include fiberglass, polymer or composite. Additionally, it is advisable to consult industry experts to help in selecting the best line guards. The following is a guide for conducting a comparative analysis for line guards in South America.

- Material and durability – they are from various materials used to produce the line guards. These include fiberglass, polymer and composite. Assess the advantages of each of these materials suiting your application.
- Insulating properties – select the best materials that offer electrical insulating properties to offer flexibility.
- Weather resistance – choose the line guards that are resistant to weather conditions such as UV exposure.
- Cost effectiveness – assess the cost effectiveness of the selected line guards. Consider the initial cost and long-term maintenance costs.
- Environmental impact – consider the environmental conditions of the selected line guard. Choose the material that are recyclable and have a lower carbon footprint.
- Application specifics – consider the type of line guard used depending on their ability to support conductor. These may include bird flight diverters, spacer dampers and corona rings.
Certifications and standards in South America
There are certifications and standards that ensure the quality, safety and effectiveness of the line guards. There are several international and regional standards that are commonly referenced. Additionally, it is important for manufacturers and users to be aware of and comply with these standards. The following are the common certifications and standards in South America.
- IEC standards – this provides standards for string insulators units for overhead lines with a nominal voltage greater than 1000V
- ANSI standards – this includes standards for composite insulators, specification for insulators and materials.
- ISO standards – this includes standards that ensure quality of the of the products for manufacturers.
- South American standards – this provides standards for various products including electrical components.
- Quality management systems – this is crucial for ensuring consistent quality in the manufacturing processes of line guards.
- Local regulations – these are standards set for various regions which vary between countries.
Regional market for line guards in South America
Market dynamics can change over time due to factors such as economic conditions, regulatory changes and technological advancements. It is therefore advisable to conduct market research and consulting industry reports. Additionally, reaching out to local industry associations, government agencies related to energy and infrastructure. The following are the factors that shape the industry market for line guard in South America.

- Demand drivers – identify the key drivers of demand for line guards as such as infrastructure development, grid modernization projects and expansion of the energy sector.
- Economic trends – examine the overall economic conditions in the region such as economic growth and investment in the energy sector.
- Technological trends – stay informed about advancements in the line guard technologies. Innovations and technological improvements may influence purchasing decisions.
- Government initiatives – explore the government initiatives or incentives that promote the use of advanced technologies in the power sector.
- Market players – identify key manufacturers, suppliers and distributions of line guards in the region. This is to gain insights into market dynamics.
Frequently asked questions
A line guard is a protective device used to maintain a safe distance between conductors. It helps to prevent unintended contact which could lead to electrical faults. They create a physical barrier between conductors and other elements.
The materials used in line guard manufacturing vary depending on the type of line guard and its intended application. These materials include polymer, fiberglass and composite materials.