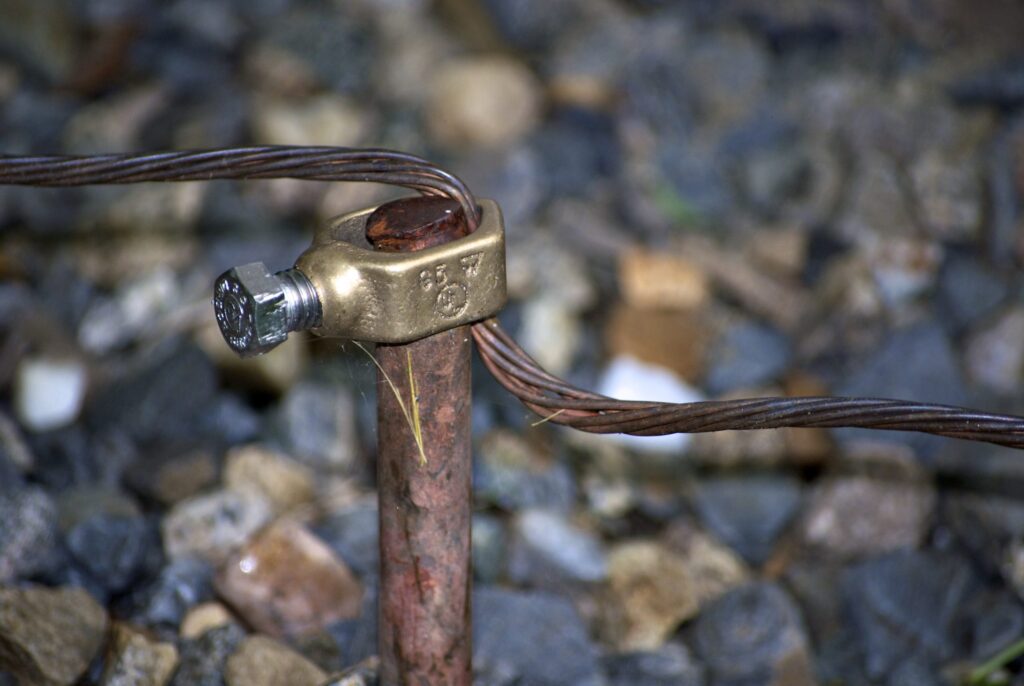

A ground rod is a component designed to provide a low-resistance path for electrical faults and lightning strikes. It helps to dissipate the surge current to the ground for safety. It also helps prevent electrical shock hazards, equipment damage and fires. Reliable ground rods play an important role in ensuring the safety and reliance of electric grid in Southeast Asia. This requires the use of materials such as copper, galvanized steel, stainless steel and composite materials. Common types of ground rod include copper ground rods, galvanized steel, stainless steel, solid copper, composite ground rods and threaded ground rod. They find use in applications such as electrical systems, industrial facilities, substations and telecommunications.
Key features of ground rod
There are various features of the ground rod that help to increase effectiveness and reliability. The availability of different features depends on various characteristics and application needs. The following are the key features of the ground rod.

- Length – the ground rods come in different lengths which depend on the depth of installation. This helps to achieve optimal grounding effectiveness in specific soil types.
- Diameter – they are also available in different diameters that affect the rod’s strength and conductivity. Common sizes are 1/2 inch and 5/8 inch.
- Surface finish – the surface finish of the ground rod impacts a good electrical connection. Common finish includes smooth, threaded or serrated finish depending on the application.
- Threaded and non-threaded – threaded ends allow for easy attachment of connectors and clamps. The non-threaded ground rods require compression connectors for secure connections.
- Conductivity – they should have high conductivity to ensure efficient dissipation of fault currents and lightning strikes into the ground.
- Installation – they should have easy installation to reduce labor costs and installation time.
- Cost-effectiveness – the costs of the rods vary depending on material and features available.
- Material – ground rods are from various materials such as copper and stainless steel. These materials provide durability and reliability.
- Driving point design – ground rods have a pointed end that allows them to drive into the ground.
- Corrosion resistance – ground rod from specific materials offers corrosion resistance. This help to increase longevity and effectiveness.
Selection and installation of ground rod
Selecting the right ground rod ensures the effectiveness and reliability of the grounding system. It involves considering factors such as soil conditions, materials and corrosion resistance, conductivity, length and diameter, driving method and costs. The installation process should ensure the safety of the electrical systems and equipment. The following is a basic installation guide of the ground rod.

- Safety precautions – follow all the safety precautions such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment. Ensure the electrical system is de-energized to ensure safety.
- Prepare the ground rod – inspect the ground rod for any defects or damage and clean to ensure good electrical contact with the soil.
- Drive the ground rod – drive the ground rod to a depth that reaches the conductive layer of soil. The depth varies depending on the soil resistivity in the area of installation.
- Exposure – leave a few inches of the ground rod above the ground surface to allow for the attachment of the ground rod clamp.
- Clamp attachment – connect the grounding conductor to the ground clamp securing to the exposed portion. This helps make good electrical contact with the rod.
- Run the grounding conductor – connect one end of the grounding conductor to the other side of the ground rod clamp.
- Grounding electrode conductor – connect the grounding conductor to the grounding electrode conductor.
- Bonding and additional ground rods – ensure all ground rods are interconnected and bonded together according to the local codes and standards.
- Inspection and testing – visually inspect the entire grounding system for proper connections and grounding integrity.
- Documentation – keep records of the installation including the location of the ground rod, materials used and any test results.
Maintenance and inspection of ground rod
Proper maintenance and inspection of the ground rods ensure the effectiveness of the grounding system and electrical safety. This is because ground rods degrade over time due to environmental factors, corrosion and wear. It helps ensure effective protection against electrical faults and lightning strikes.Additionally, it is advisable to include professional maintenance and inspection f the ground rod. The following is a basic guide to maintenance and inspection of ground rods.
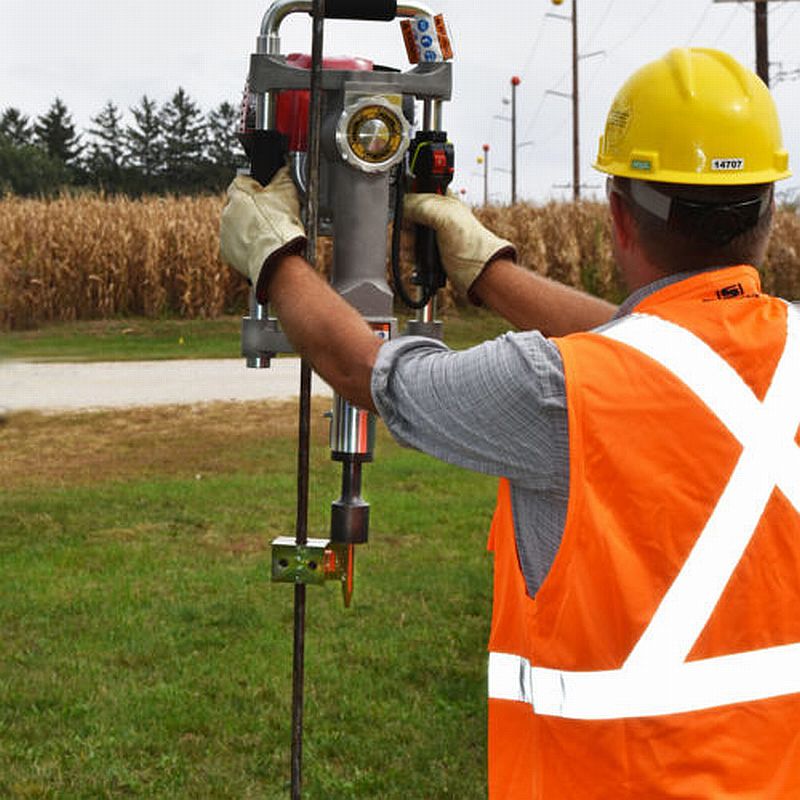

- Perform visual inspections to check for signs of damage, corrosion or loose connections.
- Check for corrosion on the surface of the ground rod which can lead to reduced conductivity.
- Assess the connections between the ground rod, clamps and grounding conductors. Tis helps to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
- Inspect the grounding electrode conductor for signs of wear, damage or loose connections at both ends.
- Apply anti-corrosion on the surface of the ground rod to help extend the lifespan.
- Use the suitable torque values to tighten any loose connections to ensure proper clamping.
- Regularly clean the surface of the ground rod to remove dirt, debris and contaminants that may hinder electrical conductivity.
- Periodically test the ground resistance of the grounding system to measure the resistance to ground.
- Maintain detailed records of inspection, tests and maintenance for future use.
Comparative analysis of ground rods in Southeast Asia
A comparative analysis involves evaluating and assessing different types and designs of ground rods in the market. It depends on factors such as materials, performance, cost and suitability for the region’s specific environmental conditions. Additionally, it is advisable to conduct the comparative analysis in the local market. The following are the key factors to include in a comparative analysis.

- Material – common materials for ground rod include copper, galvanized steel, stainless steel and composite materials. Assess the advantages of each of these materials and how they suit your application needs.
- Performance – there are several factors that influence the performance of ground rods in various applications. These include conductivity, corrosion resistance and soil compatibility.
- Costs – consider the cost of each ground rod depending on the material used. Select durable materials and balance with the performance and application needs.
- Environmental factors – consider the specific environmental challenges of the installation area. These may include high humidity, temperature extremes and exposure to saltwater.
- Local regulations and codes – ensure the selected ground rods comply with the local standards. They should also meet the requirements of the region in terms of installation and performance.
- Maintenance and durability – assess the required maintenance needs of the different ground rods materials.
- Expert advice – consult with the local electrical professionals or grounding experts for valuable insights into the best ground rods to select.
Certifications and standards in Southeast Asia
There are several standards and regulations that govern the use of ground rods in Southeast Asia. These standards vary by country within the region. Some of the countries in this region adapt to most of the international standards and regulations. Also, ensure the selected ground rods complies with the relevant standards and certifications in the region of installation. The following are the common standards and regulations related to ground rods in Southeast Asia.
- IEC standards – these are standards that address lightning protection system components. They provide guidance for ground rods design and testing.
- ASTM standards – these standards provide specifications for copper and coper-clad steel grounding rods.
- Local electrical codes – these codes vary between countries and may incorporate international standards.
- IEE wiring regulations – these regulations may include provisions for grounding and bonding for grounding rods.
- ISO certifications – these helps manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to quality management systems.
- Product certifications – check for product certifications from reputable organizations and testing laboratories.
Regional market for ground rod in Southeast Asia
There are various factors that influence the regional market and demand of ground rods in Southeast Asia. Some of these factors include industrial growth, infrastructure projects and the demand for reliable electrical systems. Additionally, it is advisable for manufacturers to assess the market to tailor their offerings to local requirements. The following are the common factors that shape the regional market for ground rods in Southeast Asia.

- Economic growth – the economic growth leads to increased infrastructure development. This includes commercial and residential construction, industrial facilities and transportation networks. Ground rods help ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
- Natural disaster vulnerability – disasters such as thunderstorms lead to the increased demand for lightning protection systems.
- Competition – competition from local manufacturers and international suppliers increase the availability of ground rods in the market.
- Electrification initiatives – electrification of rural areas create opportunities for ground rods installations in the region.
- Environmental conditions – Southeast Asia experiences conditions such as tropical climate and high humidity which may lead to corrosion of grounding components.