
A distribution grip dead end is a way of fastening and supporting cables or conductors. It functions in electrical installations, transmission systems, and telecommunications networks. It is also useful for terminating the end points of a conductor within the system. The dead end grips keep the wires in place, preventing sagging or strain on them. The distribution grip is a sort of cable grip that can grab cables of various forms and sizes. This allows them to accommodate various types and sizes of wires. The dead end is the point at which a cable terminates and connects to a terminal or piece of equipment. Dead ends aid to route and secure cables in an installation.
Fittings for distribution grip dead end
Distribution grip dead ends are compatible with various attachments. These fittings contribute to their reliability. The accessories used differ according to the installation’s requirements and the type of cable used. They also help to ensure that wires are properly installed, supported, and protected. The following are common attachments for distribution grip dead ends.
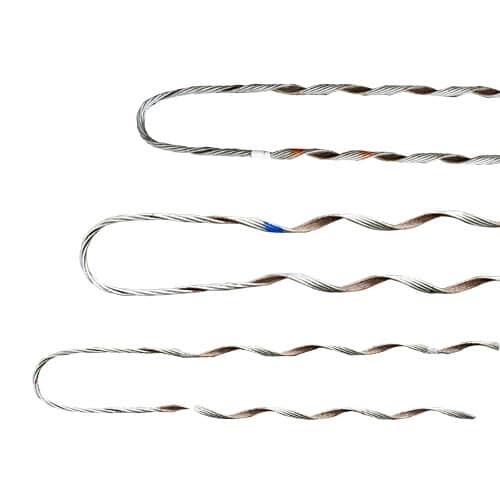

- Thimbles – these are metals inserted inside the loop of a dead end. They serve to keep the cable from abrasion and damage. They create a smooth surface for the cable to bend around, lowering the danger of injury.
- Strain relief clamps – these help to relieve strain on cables by dispersing the load throughout their length. Installation tools – several tools are necessary to install and tension distribution grip dead ends. These include cable pullers, tensioning devices, and cutting instruments.
- Insulation – imaterials contribute to electrical insulation and environmental protection. The materials used vary by the application and installation requirements.
- Supporting hardware – this consists of brackets, screws, and other hardware used to install and support dead ends.
- Protective coating – a variety of coatings work to distribution grip dead ends and accompanying gear. They help to keep the components free of rust and corrosion.
- Preformed line products – these include clevises, rods, plates, and other hardware components. They aid to anchor and attach the dead end to the structure.
Advantages of applying a distribution grip dead end
Distribution grip dead ends offer many benefits for electrical and data communication installations. The dead end grips contribute to a more efficient, dependable, and secure electrical and data connection infrastructure. The following are some common advantages of employing a distribution grip dead end.

- Secure cable support – dead ends offer a secure way to support cables near termination points. This prevents cables from sagging or drooping, which can cause strain, damage, or interference with other components.
- Improved cable management – dead ends help to organise and manage cables by providing a fixed termination point. This makes it easier to route and manage cables throughout the installation.
- Infrastructure longevity – this is by preventing cable damage and providing enough cable support. This helps to reduce maintenance costs and downtime caused by cable failures.
- Installation ease – many dead end grips have designs to install with minimal tools and work. This saves time and resources throughout the installation procedure.
- Reduced cable damage – distribution grip dead ends lessen the chance of abrasion, twisting, and other types of damage. This can occur during installation or as a result of environmental conditions such as wind or vibration.
- Enhanced safety – proper cable installation can reduce the likelihood of accidents or injuries caused by unsecured cables. The dead end grips can help keep the cables properly supported and maintained.
- Flexibility and adaptability – distribution grip dead ends come in a variety of sizes and styles. This helps to hold various sorts and sizes. The versatility enables for customisation to match the installation’s individual requirements.
Technical requirements for distribution grip dead ends.
Technical standards for dead end grips differ depending on some factors. This includes information such as the type and size of cables utilized, as well as the application. The requirements help to guarantee that dead ends are effectively selected and placed. Also, the producer should supply technical data for the chosen dead end grips. The following are the technical requirements for distribution grip dead ends.
| Catalog Number | Diameter Range (Inches) Min | Diameter Range (Inches) Max | Units | Wt./Lbs. | Length (Inches) | Color Code |
| DG-16 | .182 | .203 | 100 | 14 | 16 | Blue |
| DG-17 | .229 | .257 | 100 | 20 | 17 | Orange |
| DG-24 | .290 | .325 | 100 | 33 | 24 | Red |
| DG-26 | .326 | .364 | 100 | 44 | 26 | Green |
| DG-28 | .410 | .460 | 25 | 31 | 28 | Blue |
| DG-32 | .461 | .516 | 25 | 22 | 32 | Orange |
- Cable compatibility – requirements should cover a range of cable sizes and types. They may include information about the least and greatest cable diameters, as well as appropriate cable materials.
- Material – the specifications should include the material composition of the distribution grip dead end. They should contain information about any protective coatings or finishes. These are mostly used to increase durability and corrosion resistance. Common materials include stainless steel, galvanized steel, and aluminum.
- Environmental rating – dead ends ought to be designs for use in specified environmental conditions. Environmental ratings should consider interior and outdoor applications. They also include places with high temperatures or those exposed to moisture or chemicals.
- Dimensions and weight – the specs should contain the dead end’s precise dimensions and weight. This facilitates accurate size and selection for the specified installation.
- Load rating – the dead ends have ratings for the highest load capacity, which shows how much stress or weight the grip can withstand. Load rating standards change depending on a variety of circumstances.
Industry developments and improvements for dead end grips
Distribution grip dead ends are now upgraded and updated to improve performance, dependability, and convenience of installation. These developments represent continued industry initiatives. Additionally, it is advisable to investigate the technologies employed in the production of the chosen distribution grip dead end. Here are some industry advances and updates for dead end grips.

- Material innovation – manufacturers continue to explore new materials and coatings for the dead ends. These materials help to enhance the durability and corrosion resistance. These helps provide protection against environmental factors.
- Enhanced design features – the dead ends have features that optimize cable grip, distribution of load and ease of installation. New grip designs include serrated jaws to enhance grip strength and reduce slippage.
- Compatibility with advanced cabling systems – distribution grip dead ends advance to accommodate new cabling systems. They support higher speeds and bandwidths such as fiber optics and high speed ethernet cables.
- Integration of smart technologies – this is including embedded sensors or RFID tags. This is to enable real-time monitoring of cable tension and temperature. This allows for easy maintenance to prevent cable failures and optimize performance.
- Enhanced load ratings – dead end grips have designs to support greater loads. This is while maintaining safety and reliability. Advancements in materials allows for higher load ratings without sacrificing durability.
Applications of distribution grip dead ends.
Distribution grip dead ends function in a variety of industrial applications. They provide support, strain relief, and secure connections for the wires. The grips have several applications, which are as listed below.
- Telecommunication networks – the dead ends help to support and terminate fiber optic cables, coaxial cables and other cables. They install on aerial lines, guy wires and cable trays to ensure proper cable management.
- Overhead power distribution lines – the grips secure and support the conductors in power distribution lines. They ensure the reliable transmission of electrical power from substations to consumers.
- Guy wire support – grip dead ends aserve to secure the guy wires or guy strands. These help to provide extra support and stability to structures.
- Railway and transportation – dead ends help to support and secure cables along the rail tracks and overhead catenary systems. They help maintain reliable communication and power distribution for safe and efficient operation.
- Renewable energy projects – they work in applications such as wind farms and solar installations. They help to support and terminate cables connecting turbines, solar panels and power distribution.
Frequently asked questions
A distribution grip dead end is a device used in electrical and data communication installations. It helps to support and terminate cables at their endpoint. It also helps to prevent sagging and damage to cables while ensuring proper cable management.
Technical factors for distribution grip dead ends may include cable compatibility, load rating, material composition and installation requirements.
Recent advancements in distribution grip dead ends include material innovations, improved design features and enhanced load ratings.