A tension clamp is a component used on power line systems to provide tension and support the conductors. They are also known as strain clamps or dead-end clamps. Tension clamps install at the ends of a span or at intervals along the power line to maintain proper tension in the conductors. The tension clamps secure the conductor and resist the tension forces. These forces arise from weight of the conductors, wind loading and external factors. They are from materials such as galvanized steel or aluminum alloy. These materials helps them withstand mechanical stresses. Tension clamps features components such as bolts or wedges to allow for tension adjustments during installation. They work in application such as power line systems, telecommunications, industrial applications and cable television lines.
Components of tension clamp for power lines
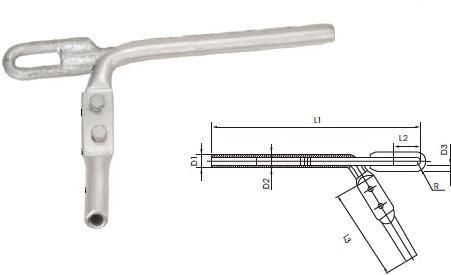
Tension clamps consists of several components working together to secure and maintain tension in the conductors. Moreover, components available vary depending on the specific requirements of the application, design and size of conductor and different manufacturers. The following are the main components of the tension clamps for overhead power lines.
- Body – this is a metal structure that houses and supports the other components. Its design is to withstand the mechanical forces in overhead power line installations.
- Gripping elements – tension clamps feature gripping elements that holds the conductor in place. It include grooves, jaws or serrated surfaces. They provide a strong grip on the conductor to prevent slippage.
- Fasteners – bolts, nuts and washers are the common fasteners used to secure the tension clamp around the conductor.
- Tensioning adjustment mechanisms – tension clamps use tension adjustment mechanism to allow proper tensioning of the conductor during installation and maintenance.
Types of tension clamp for overhead power lines
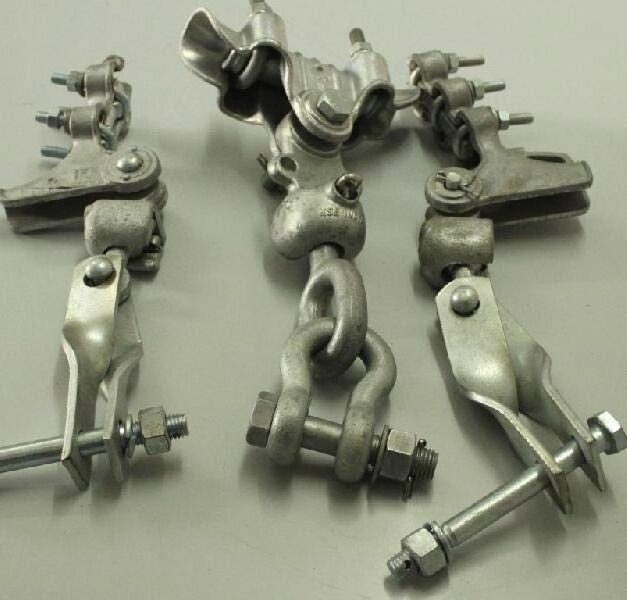

Each type of tension clamps has unique designs to meet the specific requirements of the overhead power lines. These may include conductor sizes, configurations and installation requirements. The following are the common types of tension clamps used for overhead power lines.
Bolted tension clamps – this type of tension clamps has two pieces, the body and the keeper bolted together. They allow easy installation and adjustment of the tension.
Compression-type tension clamp – these clamps use compression fittings or sleeves to secure the conductor. These are commonly used for aluminum conductors.
Automatic tension clamps – these are also known as self-adjusting tension clamps. They help maintain a constant tension in the conductor. They offer convenience and continuous tension control without the need for manual adjustments.
Wedge-type tension clamps – these clamps use wedges to provide a secure grip on the conductor. These are commonly used for larger conductor sizes and higher tension applications.
Armor rod tension clamps – these clamps use armor rods to provide additional support and protection to the conductor. They reduce stress and enhance the grip of the tension clamp.
Applications of high-tension strain clamps
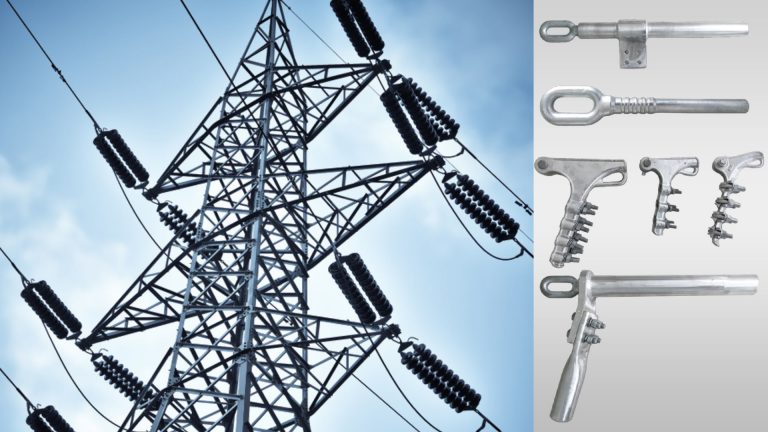

High-strength tension clamps find uses in various applications in the industry due to their capabilities. They should meet the specific requirements and characteristics of the power line system. The following are the common application areas of tension clamps.
- Overhead distribution lines – tension clamps work in distribution lines to help maintain tension in the conductors, ensure proper alignment, minimize sag and facilitate the reliable distribution of electrical power consumers. They work in medium voltage and low voltage distribution networks.
- Crossings and river crossings – tension clamps work at points where power lines pass over other power lines, roads, railways or rivers. Additionally, they ensure proper tensioning and support of the conductors to maintain the necessary clearance.
- Overhead fiber optic cables – tension clamps help to secure and tension the fiber optic cables. This ensures proper alignment, protection and reliable transmission of data signals.
- Industrial applications – tension clamps provide secure anchoring and tensioning of the conductors to prevent them from sagging.
- Tower connections – the clamps work between the conductors and transmission towers to secure the conductors to the tower. Also, this helps to distribute the tension forces and ease a reliable electrical and mechanical connection.
- Overhead power lines – tension clamps work at line taps, high-tension power lines and at angled installations. They help maintain the integrity of the power line systems.
- Telecommunication lines – the clamps work in telecoms to help establish the proper tension for efficient data transmission.
Installation of tension clamp in power lines
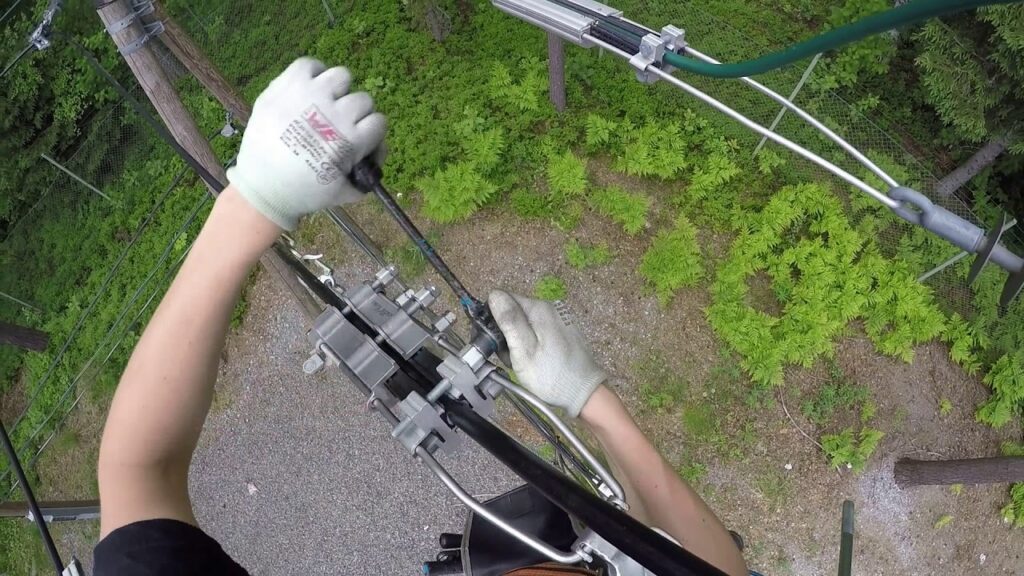

Installation process of the tension clamps vary depending on the design and manufacturer recommendations for the tension clamp. Additionally, it is advisable to follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines for safe and secure connections. The installation process should follow applicable industry standards and regulations. The following is a basic procedure for installing the strain clamps.
- Prepare the equipment and tools needed for the installation. These include tension clamps, fasteners and insulating components.
- Ensure safety by wearing personal protective equipment such as gloves, safety glasses and suitable clothing.
- Clean the conductor to remove debris, dirt or corrosion that may hinder grip of the tension clamp.
- Determine the appropriate location to install the tension clamp. Therefore, they are usually at dead-ends, line taps, tower connections or other positions.
- Place the clamp around the conductor at the desired installation point and ensure the gripping elements align properly with the conductor surface.
- Insert the fasteners int the tension clamp body and tighten them using the suitable tools.
- Use the provided adjustment mechanism to achieve the desired tension level in the conductor.
- Install the insulating components between the conductor and the supporting structure if applicable. Also, ensure the insulation provides the necessary electrical isolation and protection.
- Verify that the tension clamp is securely fastened and the conductor is properly installed and aligned. Check for signs of damage, misalignment or loose connections.
- Maintain proper documentation for the installation including dates, location and any other observations.
Selecting the best tension clamps
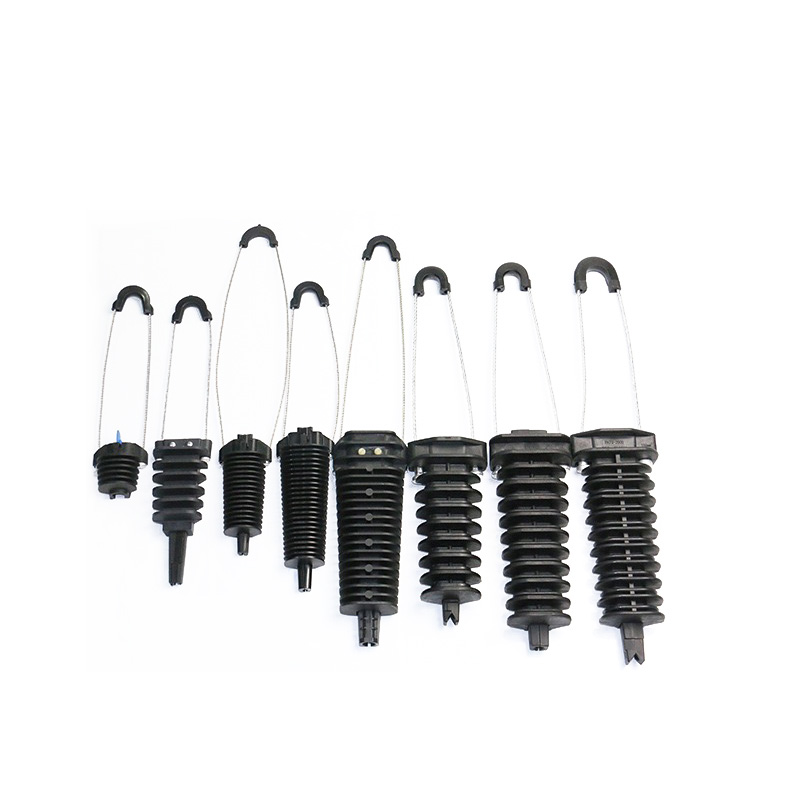

The selected strain clamp should meet the specific requirements of the application. There are various manufacturers and suppliers with different types, sizes and designs of the tension clamps. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with industry professionals for guidance on the best clamp to use depending on your application. The following are some of the key factors to consider when selecting tension clamps.
- Evaluate the cost of the tension clamps and compare from different manufacturers and suppliers. Consider the quality, initial cost, maintenance and repair costs.
- Check the ease of installation and maintenance of the tension clamps. Consider factors such as accessibility, required tools and installation procedures.
- Determine the size, type and configuration of the conductors to check for compatibility.
- Evaluate the load capacity of the tension clamps which should be able to withstand the mechanical loads. Also, mechanical loads are from the weight of the conductors and winds.
- Consider the tension requirements of the system and ensure the selected clamps can provide the necessary tension support for the specific application.
- Consider the reputation and reliability of the tension clamp manufacturer. Additionally, they should have a track record of producing high quality products.
- Check the environmental conditions considering factors such as temperature variations, humidity, exposure to UV radiation and corrosive elements.
Frequently Asked Questions