A spool tie is a device that attaches wires to insulators on poles or towers. It contributes to the stability and reliability of the electrical power transmission system. It is a generic wire component used to attach electrical conductors to spool-type insulators. A spool tie’s cylindrical design allows it to wrap around both the conductor and the insulator. This design simplifies installation and improves reliability. The spool ties comprise of the same material as the conductor to ensure compatibility and prevent abrasion. These materials include aluminum, galvanized steel, and aluminum-clad steel. Spool ties serve to attach conductors, support loads, and maintain electrical insulation. Spool ties also ensure that conductors are properly attached, reducing the danger of them breaking loose.
Key qualities of a spool tie
Spool ties come in a variety of designs and requirements for securing electrical wires to insulators. They have various qualities that make them useful for a variety of industrial applications. These attributes provide dependability, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. The spool tie has the following important features.

- Preformed design – the tie manufactures in specific shapes and sizes . This allows them to fit precisely around both the conductor and the spool insulator. This design allows the spool ties to simplify the installation process.
- Material compatibility – spool ties are from the same materials as the conductor. The materials include galvanized steel or aluminum-clad steel. These materials reduce the risk of galvanic corrosion.
- High tensile strength – the spool ties are able to withstand mechanical stresses. This is including tension and compression. They ensure the conductor remains attached to the insulator. They also distribute mechanical loads across the insulators to reduce stress points and reduce risk f failure.
- Electrical conductivity – they also provide a good electrical connection between the conductor and insulator. They help to ensure continuous electrical conductivity for reliability of power transmission.
- Secure grip – spool ties are able to grip the conductor, prevent slippage and maintain the position of the conductor on the insulator. They are resistant to environmental factors like wind, ice and temperature changes.
- Versatility – they are available in different configurations to accommodate various conductor sizes and types of spool insulators. They work in low voltage distribution lines to higher voltage transmission systems.
- Insulation properties – spool ties support the insulation provided by the insulator. This is by keeping the conductor in place. They help maintain the dielectric integrity of the insulator to prevent electrical discharge.
- Cost effectiveness – the durability and reliability of spool ties lead to lower maintenance costs. They also reduce labor costs and time which makes them cost effective.
The parts of spool tie
A spool tie’s design and components are specifically engineered to offer reliable mechanical and electrical connections. Each spool tie component has a distinct purpose that helps to ensure the power system’s reliability. Also, these components ensure that the spool tie makes a secure, long-lasting, and effective connection with conductors. The essential components of the spool tie are as listed below, along with their purposes.
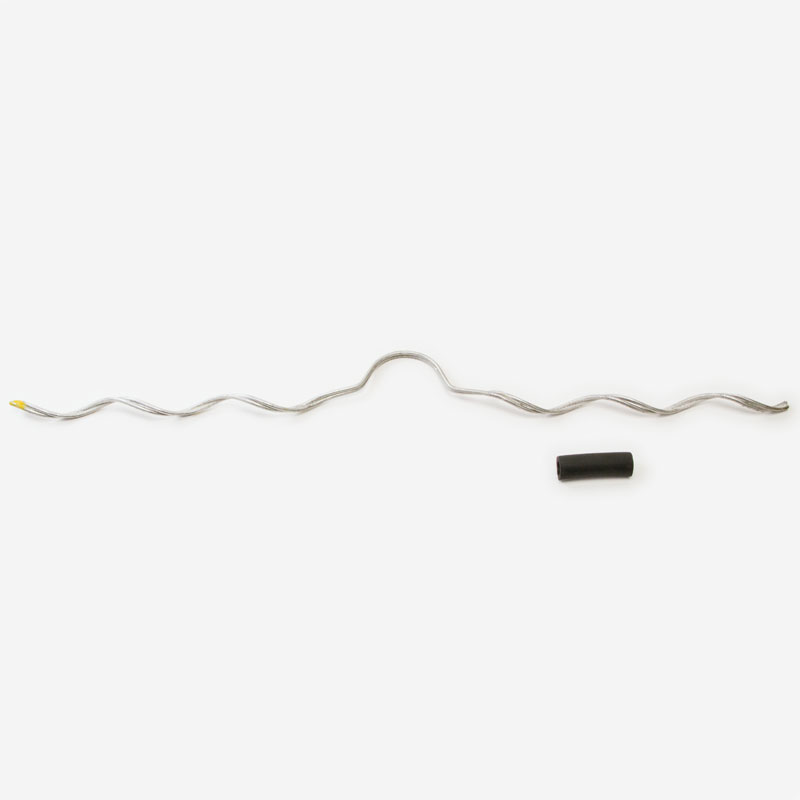

- Preformed wire body – this is the main component of the spool tie which is from metal wire. It is pre-shaped to fit around the conductor and the spool insulator. Its function is to wrap around the conductor and the insulator to provide a firm grip.
- Helical legs – spool ties have helical legs that extend from the preformed wire body. The legs wrap around the conductor to secure the conductor to the insulator. This wrapping technique ensures a tight, slip-resistant fit that withstands environmental forces.
- Gripping sections – the sections of the spool tie that are un contact with the conductor have gripping features such as notches or ridges. These features enhance the tie’s ability to grip the conductor to prevent movement and ensure stable connection.
- Central groove – this is a groove at the center of the spool tie that fits around the insulator’s neck. This section secures the spool tie to the insulator and ensures proper aligning and positioning.
- Material composition – the spool tie materials matches the conductor’s material. This is to ensure compatibility and reduce the risk of corrosion.
Specific kinds of Spool Ties
Spool ties are available in a variety of forms and styles to suit specific needs and environments. Their primary function is to attach conductors to spool insulators in overhead transmission lines. The categories differ their construction, application, and level of security. Also, selecting the correct spool ties guarantees that the power system is reliable, safe, and efficient. The following are the most prevalent forms of spool ties.

- Standard spool tie – this consists of a preformed wire body with helical legs that wrap around the conductor. It works in standard overhead line applications that experience mechanical stress. They are easy to install and provide secure grip on the conductor.
- Heavy-duty spool tie – these have a thicker and more robust wire than standard spool ties. These ties include extra gripping features for environments with high mechanical stress.
- Insulated spool tie – these ties use an insulating layer around the wire to prevent electrical conductivity. They serve in applications where electrical insulation between the conductor and the tie is necessary. They prevent electrical faults and ensures safe operation in areas with potential for electrical arcing.
- Adjustable spool tie – these have adjustable elements that allow for length modifications to fit various insulator sizes. They work in situations that need flexibility in fitting different conductor sizes.
- Preformed spool tie – this is pre-formed to fit specific conductor sizes and insulator type and provide a custom fit. They serve in standard power line installations where consistent performance is crucial. They also provide reliable, secure and tailored fit for specific applications.
- Reinforced spool tie – this includes extra reinforcement such as extra wire strands or thicker body. They are ideal for installations that need high mechanical strength.
Areas of application for spool ties
Spool ties are versatile components used in transmission and distribution systems. They ensure that electrical connections are stable and reliable. The spool ties can withstand environmental and mechanical forces. This makes them necessary components. Additionally, they help to preserve the stability and efficiency of electrical power systems. Spool ties have the following applications.

- Distribution and transmission lines – spool ties work in low, medium and high voltage transmission lines. They work where conductors need fastening to insulators. This is to maintain proper clearance and tension.
- Rural and urban power systems – spool ties are essential in maintaining the stability and long-span lines. They help to manage the complexity of power lines running through congested areas.
- Temporary and emergency installations – spool ties serve in temporary installations where quick and secure conductors attachment is necessary.
- Severe weather and high wind areas – spool ties provide reliable conductor attachment. This helps to prevent dislodging or damage of the conductors. They work in areas with high wind loads where maintaining conductor stability is critical.
- Vibration and Aeolian vibration control – the ties can have features that help dampen vibrations. The spool ties help manage Aeolian vibrations which can cause conductor fatigue and damage.
- Utility pole infrastructure – spool ties serve in utility pole infrastructure to secure conductors in vertical and horizontal configurations. They also serve where many conductors attach to insulators mounted on Crossarms.
- Renewable energy projects – spool ties serve to secure conductors to insulators in areas exposed to high winds. they also help manage and secure conductors in exposed and elevated positions.
- Grid maintenance and upgrades – spool ties aid in routine maintenance and upgrades. They help to resecure conductor attachments or repair.
Advantages of employing spool ties in overhead transmission lines
The use of spool ties in overhead transmission lines has various benefits that improve dependability and safety. They are adaptable and resilient, making them critical to the integrity of power systems. The following are the advantages of employing spool ties.

- Secure and reliable conductor attachment – spool ties provide a secure connection between the conductor and the insulator. This attachment reduces the risk of conductor slipping or becoming loose which can lead to power outages.
- Simplified installation – preformed spool ties have designs for easy installation and reduces the need for specialized tools.
- Enhanced mechanical strength – the ties distribute mechanical stress across the conductor and insulator to reduce wear and tear. They have design to withstand mechanical forces such as tension and compression.
- Corrosion resistance – spool ties are from the same material as the conductor to prevent galvanic corrosion. They also have coatings that protect them from environmental factors like moisture, salt and pollutants.
- Improved electrical performance – spool ties help ensure continuous electrical conductivity by maintaining a secure attachment.
Frequently asked questions
A spool tie is used to secure electrical conductors to spool insulators on utility poles or transmission towers. It secures the conductor to prevent movement and maintain the reliable electrical connections.
Spool ties’ sturdy design ensures long-term stability and minimal wear, requiring less inspections, repairs, and replacements. This durability helps to reduce total maintenance expenses.
Spool ties assist inin keeping conductors secure and stable, preventing inadvertent disconnections and electrical failures. Insulated spool ties also improve safety by preventing electrical contact and arcing.