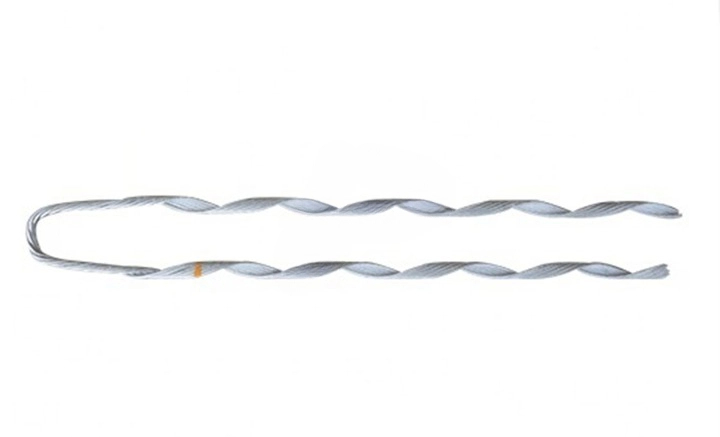

A distribution grip dead end is a component used in both electrical distribution and transmission systems. These are systems used for delivering electricity from power plants to homes and businesses. Distribution grip dead ends provide a secure attachment point for the conductors. They also help to withstand environmental factors such as wind and ice loading. They help to ensure the structural integrity and reliability of the overhead line system. The dead end grips also help to terminate the ends of overhead conductors. This helps to maintain tension in the line, support the weight of the conductors. Distribution grip dead ends also help to terminate the ends of high-voltage transmission conductors. They have designs to withstand high tension levels and mechanical stresses. Common types include bolted, compression, preformed and guy grip dead ends.
Components of the distribution grip dead end
The components of distribution grip dead ends vary depending on the specific design and manufacturer. The components work together to provide a secure and reliable attachment point. High-quality components help to maintain the integrity and performance of the distribution line. The following are the components of distribution grip dead ends.
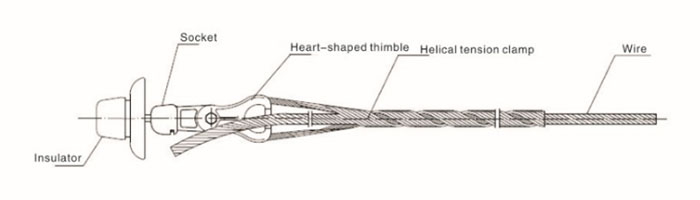
- Main body – the main body consists of a sturdy frame or housing that holds the gripping mechanism. It also provides structural support for the attachment of the conductor.
- Gripping mechanisms – this is a component responsible for holding the conductor in place. The mechanisms include serrated jaws, wedges or other features to prevent slippage.
- Attachment hardware – the dead-end grips need hardware for attachment to the support structure. This helps to fasten the dead end to utility pole or transmission towers. These include bolts, nuts, washers, clamps or straps.
- Insulating material – grip dead ends may include insulating material to provide electrical isolation. This insulation helps prevent electrical arcing and ensures the safety of the line.
- Corrosion protection – the dead-end grips may feature corrosion resistant. These help to enhance durability and longevity. This helps protect the dead end from environmental factors such as moisture and salt.
- Tension adjustment mechanism – distribution grip dead ends include a tension change mechanism. This allows for fine-tuning of the tension applied to the conductor.
- Labelling and markings – dead end grips may have labelling with information. This is including manufacturer specifications, part numbers or installation instructions.
Materials used in construction of distribution grip dead end
Distribution grip dead ends are from materials that provide mechanical strength, durability and suitability. The choice of material depends on various factors. These include application requirements, environmental conditions and cost considerations. The following are the common materials used in the construction of distribution grip dead ends.

- Steel – this is the most used material for distribution grip dead ends. This is due to its high strength and durability. Steel dead ends are able to withstand the mechanical stresses and loads. It may also have coating or galvanized to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Aluminum alloy – aluminum dead end grips are lightweight yet strong. They also offer good corrosion resistance with help from protective coatings.
- Stainless steel – this provides excellent corrosion resistance especially in harsh or corrosive environments.
- Bronze – this is a copper alloy that provides good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. It may also serve for its aesthetic appeal and resistance to wear and tear.
- Composite materials – some of the dead ends may have composite materials for their lightweight and corrosion resistant properties.
- Insulating materials – the dead ends may have insulating materials like plastics or rubber. They prevent electrical conductivity between the conductor and the support structure.
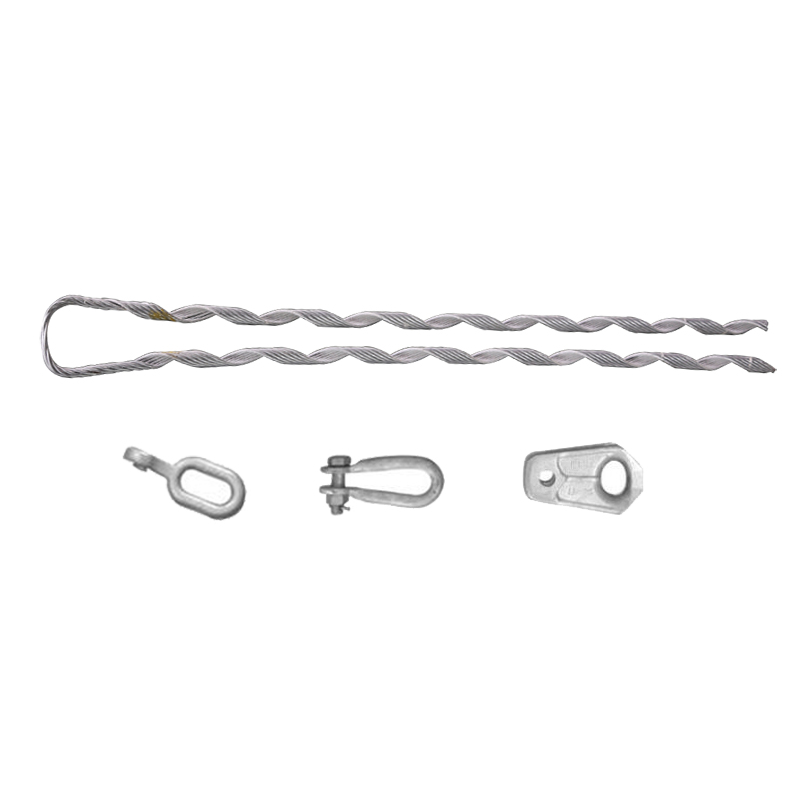
Accessories used with distribution grip dead ends
There are several accessories or fittings that work with distribution grip dead ends. This aims to ease installation, enhance performance and ensure safety. Additionally, it is important to select the right accessories depending on the needs of the application. The following are the common accessories used with distribution grip dead ends.
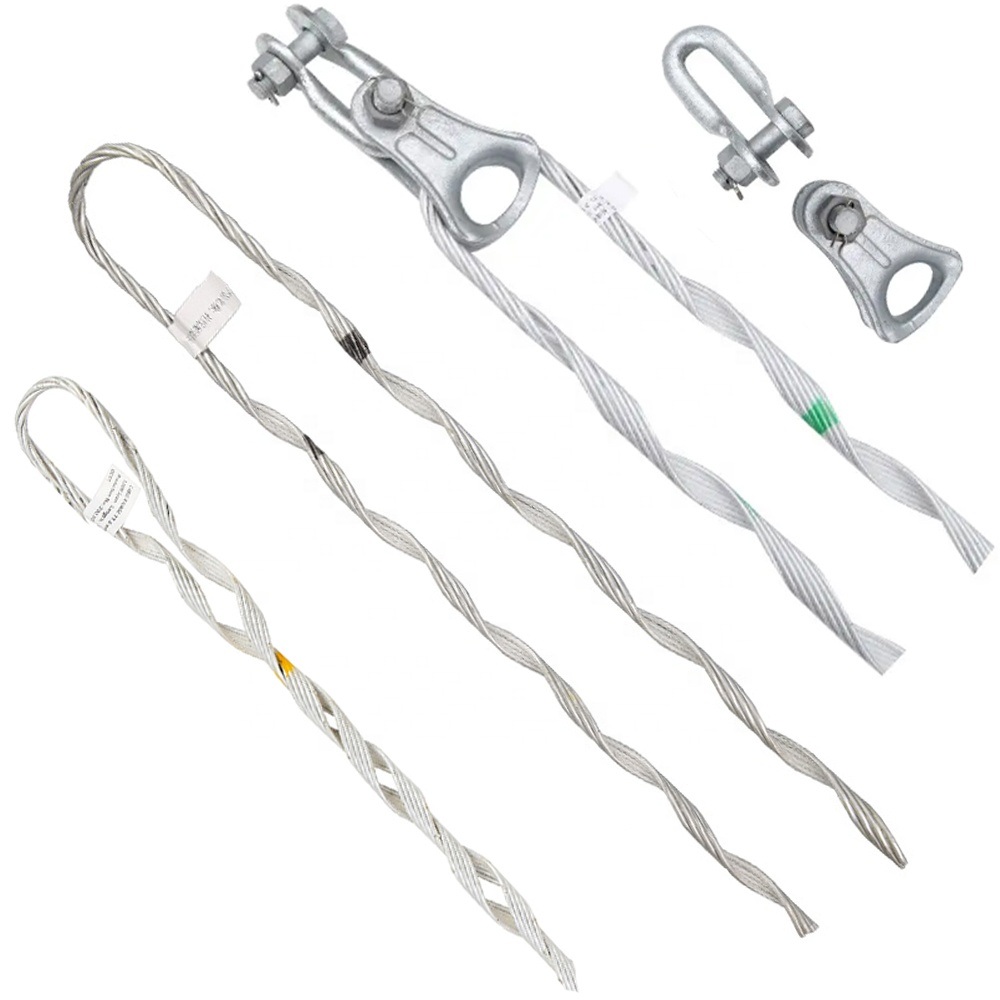
- Grips – grips are the main components of the dead end and serve to hold the conductors in place. They have various designs including helical grooves, serrated jaws or clamps.
- Preformed rods – preformed rods are metallic rods or strands that help to reinforce the grip. They provide extra strength and stability to the grip dead end assembly.
- Installation tools – this is including wrenches, sockets, torque wrenches and tensioning tools. These help to ensure proper installation and tightening of bolts, nuts and other fasteners.
- Thimbles – these are metal sleeves or loops inserted into the grip dead end assembly. It provides a smooth surface for the conductor to pass through. This prevents the grip from directly contacting and damaging the conductor.
- Suspension insulators – these work with dead end grips in suspension-type distribution lines. They provide electrical isolation and mechanical support.
- Connecting links – these are connecting components used to attach the grip dead end assembly to the supporting structure. They are from strong and corrosion-resistant materials like steel.
- Anti-theft devices – these are devices installed on distribution grip dead end to prevent theft of vandalism. These devices help protect the integrity of the distribution line and prevent unauthorized access to electrical infrastructure.
- Cotter pins – these are small metal fasteners used to secure and lock the component of the grip dead end assembly together. They prevent the grips, preformed rods and armor rods from coming loose.
Distribution grip dead ends for ADSS/OPGW cables
Distribution grip dead ends work in ADSS and OPGW cables to terminate the cables in electrical distribution systems. ADSS and OPGW cables work in telecommunication, data transmission and electrical distribution lines. Additionally, these dead ends help to ensure the safe and reliable operation of telecommunications and data transmission networks. The following is the adoption of distribution grip dead ends in ADSS and OPGW cables.

ADSS distribution grip dead ends
ADSS cables have designs to be self-supporting. Distribution grip dead ends for ADSs cables have designs to accommodate the unique construction and installation requirements. The dead ends have a gripping mechanism that holds the ADSS cable. It secures the cable without damaging its optical fibers. Distribution grip dead end may incorporate features such as insulating materials to provide electrical isolation.
OPGW distribution grip dead ends
OPGE cables provide both electrical grounding and optical fiber communication capabilities. The distribution grip dead ends for OPGW cables are able to accommodate the combined electrical and optical functions of the cables. They also have a gripping mechanism that holds the OPGW cable. It does this while maintaining electrical continuity. Distribution grip dead ends for OPGW may have features such as corrosion-resistant materials to protect against environmental factors.
Factors influencing material selection for dead end grips
There are several factors that influence the selection for materials for distribution grip dead ends. Right material selection helps to ensure they meet performance, durability and safety requirements. Careful consideration of these factors can help select materials that meet the specific requirements of the application. Also, it is advisable to seek professional help whenever in doubt for the best material selection. The following are the common factors influencing material selection for distribution grip dead ends.

- Mechanical strength – the material should have enough mechanical strength to withstand tension and loads. Consider the weight of the conductor, wind loading, ice loading and tension variations.
- Electrical conductivity – the materials used for the dead ends should not interfere with the electrical conductivity. Select materials such as aluminum alloys to reduce resistance in the distribution line.
- Temperature stability – distribution grip dead ends face a wide range of temperatures from extreme cold to high heat. The material selected should maintain their mechanical properties and performance.
- Cost considerations – materials with high performance and superior properties come at a higher cost. Manufacturers should balance performance needs with budget constraints to ensure cost-effective solutions.
- Corrosion resistance – distribution grip dead ends may face exposure to moisture, salt, UV radiation and other elements. Materials like stainless steel, aluminum alloys or coated steel ensure longevity and reliability.
- Weight – the weight of the dead ends can impact installation procedures and load on the support structure. Lightweight materials help to reduce the weight of the dead ends without sacrificing strength.
- Fatigue resistance – dead end grips face cyclic loading due to wind, conductor movement and other factors. Materials with good fatigue resistance properties withstand these cycles.
- Regulatory compliance – the dead ends must follow relevant industry standards and regulations. They should comply to standards such as IEC, NESC and ISO standards.
Frequently asked questions
A distribution grip dead end is a component used to terminate the ends of conductors and attach them to the support structures. It serves to provide a secure attachment point for the conductor, support its weight and manage tension.
Materials used for distribution grip dead end include steel, aluminum alloy, stainless steel and composite materials. These materials offer mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity.
Common accessories include installation tools, guy wire grips, suspension insulators, protective coatings, spacer dampers and anti-theft devices.