
South American countries have set goals to phase out the use of coal-fired power plants to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This will help the region transition towards renewable and clean energy sources. This is also in alignment with global climate goals. For instance, Chile is leading the region in phasing out coal as part of its carbon neutrality commitment. The government collaborates with the private utilities, which provides incentives to transition away from coal and focus on renewable energy projects. But, Colombia relies heavily on coal for energy generation and exports. The country is investing in diversifying its energy mix with significant developments in solar and wind projects. A suspension clamp helps in the transmission and distribution of electricity, including coal-fired plants. It holds overhead power lines to transmission towers or poles.
A suspension clamp has a u-shaped structure that encircles the power line conductor. The clamp is made of insulating materials like porcelain or composite materials that prevent electrical arcing. The suspension clamp provides mechanical support to the power line, preventing sagging and ensuring proper alignment. It also allows for some movement of the conductor due to thermal expansion and contraction. By supporting the power lines, suspension clamps ensure the reliable and safe transmission of electricity from coal-fired power plants to consumers. Let’s look at the factors that drive the phase out of coal-fired power plants in South America. We will also look at the importance of a suspension clamp in coal generation.
Functions of a suspension clamp in coal generation
A suspension clamp plays a crucial role in the electrical infrastructure in the transmission and distribution of power. Suspension clamps ensure reliable power transmission to urban centers and industrial zones. They also support the hybrid grids as South America transitions to renewables. Suspension clamps are efficient and durable for maintaining the reliability of power systems in coal-fired power plants. The following are the functions of a suspension clamp in coal generation.
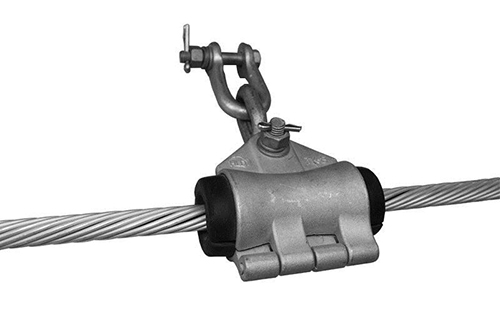
- Cable support and load distribution – suspension clamps have designs to hold power conductors in place while reducing stress. They ensure the stability of the conductor even under high tension of wind pressure.
- Vibration dampening – the clamps reduce vibrations caused by wind and other environmental factors. This protects the cables from mechanical fatigue and extends their lifespan.
- Electrical insulation – suspension clamps include insulating elements to prevent electrical faults or short circuits.
- Flexibility in line design – the clamps allow for angular adjustments and support line sag to accommodate the natural curve of transmission cables.
- Corrosion resistance – suspension clamps are made from materials like aluminum alloys or galvanized steel that withstand environmental conditions. These conditions include humidity, heat, or pollution.
Factors driving the phase-out of coal in South America
There are several factors leading to the phase-out of coal-fired power generation in South America, reflecting global trends and regional priorities. The pace of coal phase-out varies across the region due to differing economic, political, and social conditions. Discussed below are the factors leading to the phase-out of coal generation in South America.

- Environmental commitments – countries in South America are committing to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This is as part of international agreements like the Paris Accord.
- Economic factors – the cost of solar and wind energy has dropped significantly, which makes sources more competitive with coal. Policies like carbon taxes in Chile increase the financial burden of coal generation, incentivizing transitions to cleaner energy sources.
- International support and financing – development banks are providing financial and technical support for renewable energy projects.
- Grid modernization and energy security—investments in grid infrastructure and energy storage solutions support the transition to renewables. Countries like Brazil and Colombia are investing in diverse energy portfolios to reduce reliance on coal and improve energy security.
- Global influence – the push for net-zero emissions pushes the region to adopt coal phase-out timelines. The success of coal phaseouts in other regions, such as Europe, provides a framework for South America to adapt and put in place similar strategies.
- Public and corporate pressure—growing public awareness of environmental issues has increased demand for cleaner energy. Many companies in the region have voluntarily committed to reducing coal dependence, which aligns with global trends and consumer expectations.