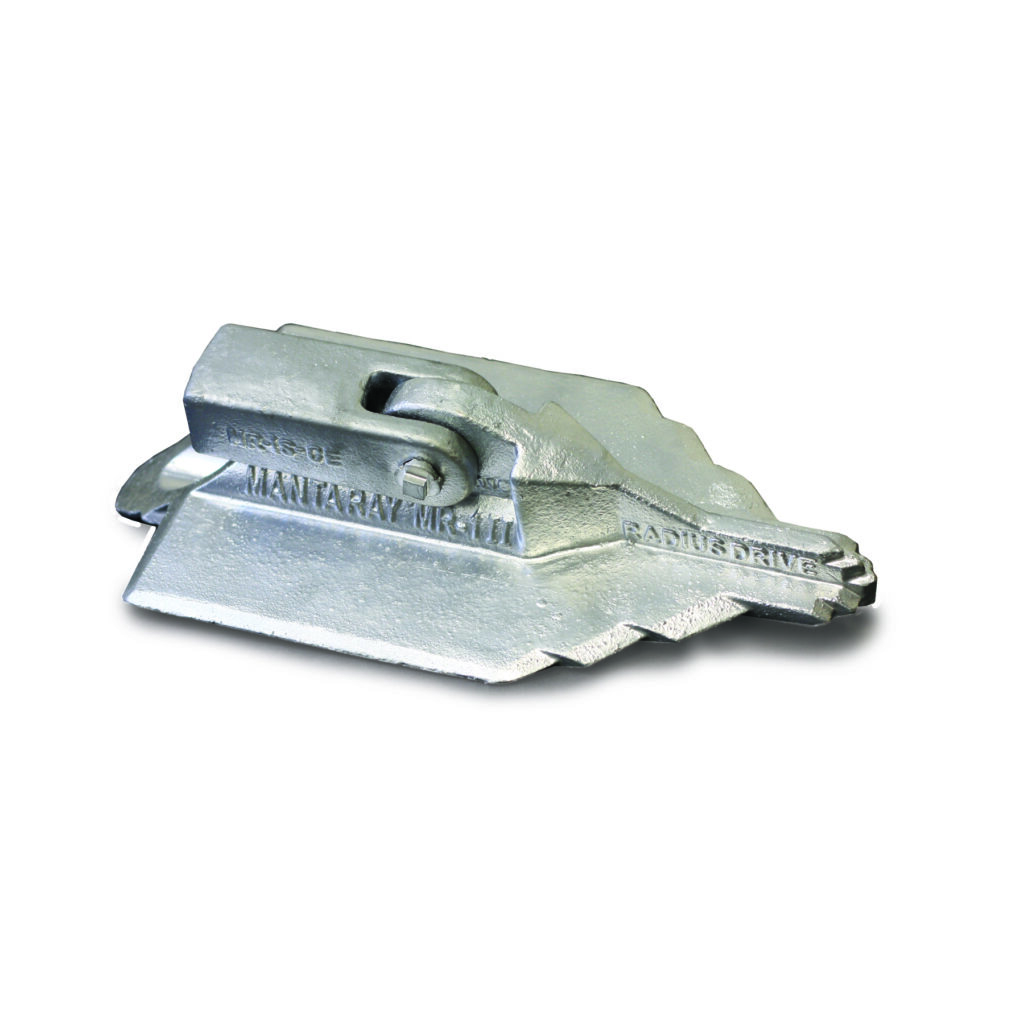

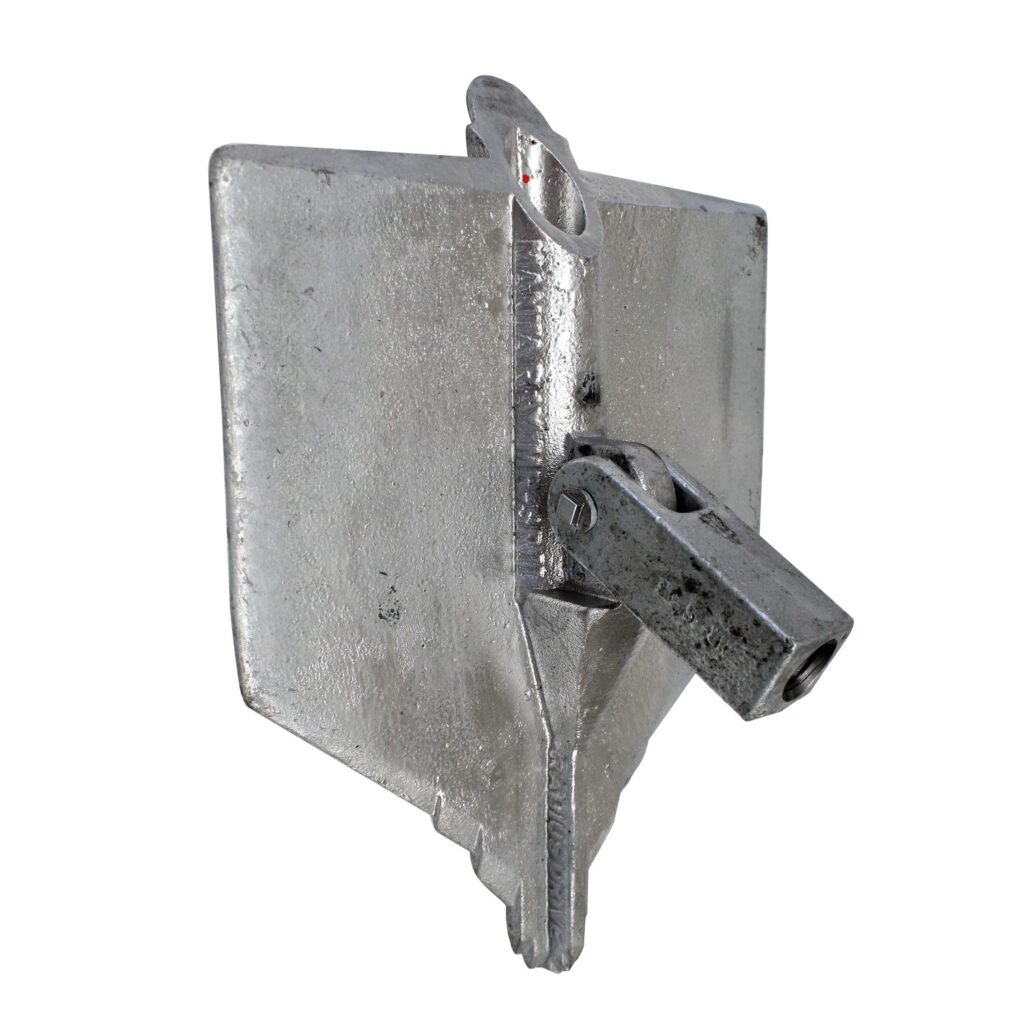
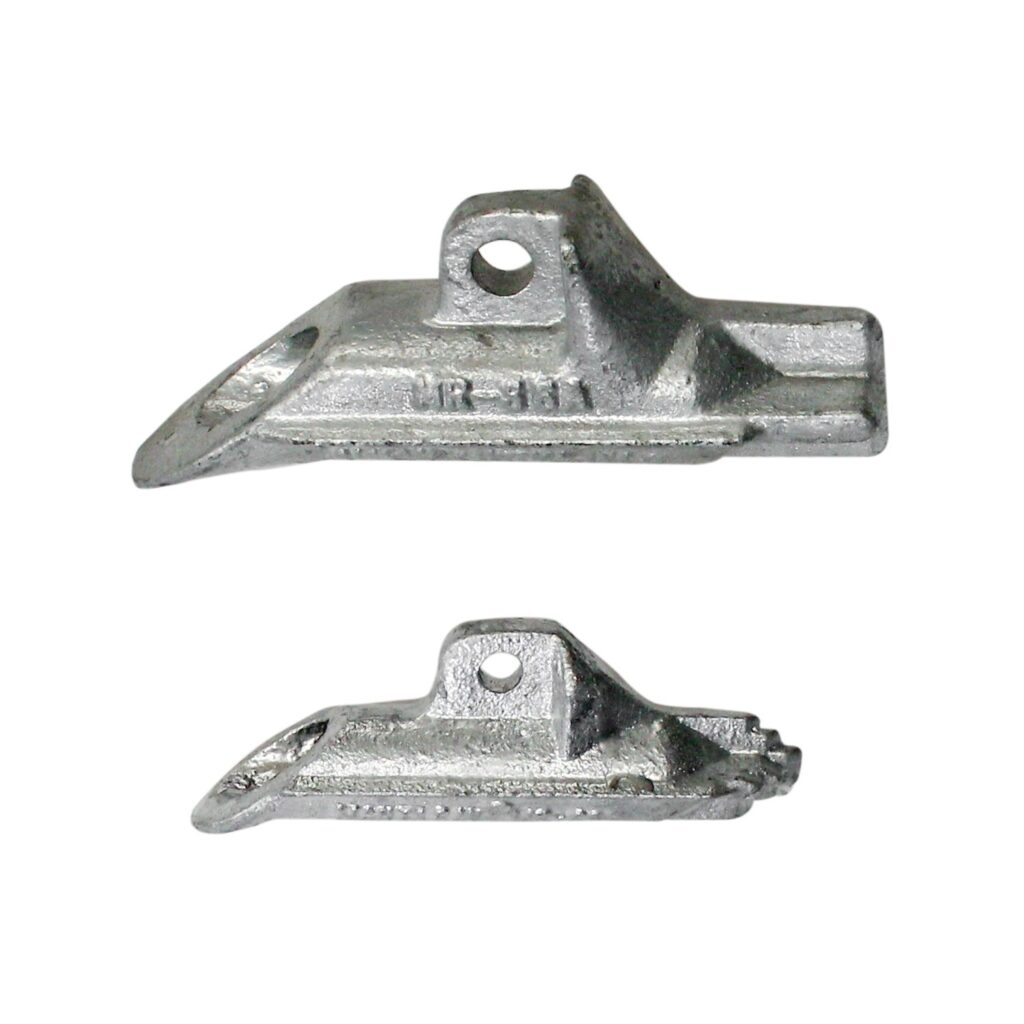
A manta ray anchor is a type of anchor used to secure transmission lines in soft or sandy conditions. It is also known as a manta ray anchor assembly. It is a large, flat anchor with a wide surface area with a large base plate with a number of flukes that extend from it. The flukes dig into the soil and provide a secure hold. It installs by digging a hole in the ground and placing the anchor in the hole. It is mostly made of steel or concrete to ensure safety and stability in the applications. These feature makes them a popular choice for use in Southeast Asian diverse climates. Common types of include standard Manta Ray, helical, expandable or wire rope Manta Ray anchor. They find use in applications such as transmission lines, utility poles, guyed towers, solar panels installations and oil and gas industry.
Key features of a Manta Ray anchor
There are various features that help provide secure and stable anchoring in various soil conditions. These features make them a popular option in a wide range of applications. The following are the key features of manta ray anchor.
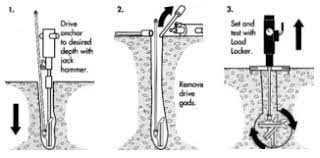
- Flat base plate – the anchor has a large, flat base plate that provides stability and load-bearing capacity. It rests on the surface or buried underground depending on the application.
- Flukes or wings – the flukes dig into the soil to provide a secure hold and resistance against uplift and lateral forces.
- Materials – they are from durable materials that ensure strength and longevity of the application. Common materials include steel or concrete that help reduce weight and improve corrosion resistance.
- Versatility – they can work in a variety of soil conditions including soft or sandy soils, harder or compacted soils.
- Load-bearing capacity – the anchors also help withstand high loads which makes them suitable for anchoring heavy structures.
- Corrosion resistance – corrosion-resistant Manta ray anchors help to ensure long-term reliability.
- Ease of installation – the anchors require standard construction equipment and procedures that simplifies the installation process.
- Removability – some of the anchors are removable which make them suitable for temporary installations.
Selection and maintenance of Manta Ray anchor
Proper selection of Manta Ray anchors helps ensure that they meet the specific requirements of your project. It depends on various factors such as project requirements, anchor types, load-bearing capacity and installation method. The installation process requires proper planning and adherence to industry best practices. The following is a basic installation process for Manta Ray anchors.

- Preparation – inspect the site to confirm the location and depth where the anchor will install. Clear the area of any obstacles or debris that may interfere with the installation process.
- Setup – set up the required equipment such as hydraulic or manual driving equipment and power drills for helical anchors.
- Anchor placement – determine the anchor spacing and layout based on the engineering calculations and project requirements.
- Anchor installation – use the appropriate tools to drill or install the anchors into the soil following the manufacturers instructions. The installation also depends on the specific type of anchor selected.
- Alignment – check the installation to ensure each anchor is correctly aligned and reaches the required depth.
- Tensioning – apply tension to the anchor and conduct suitable tests to ensure it can withstand the loads.
- Secure anchors – secure the anchor attachment points to the structure using suitable hardware.
- Compaction – backfill the hole with soil and compact it to secure the anchor.
- Records – keep detailed records of each anchor’s installation including depth, torque values and load test results.
- Inspection – regularly inspect and monitor the anchors to ensure they remain secure and are functioning as intended.
Maintenance and inspection of manta ray anchor
Proper maintenance and inspection help to ensure their long-term performance and the safety of the structures. It also helps identify and address issues early and prevent potential problems of the installation. The schedule depends on factors such as type of anchor, environmental conditions and industry standards. The following is a basic guide for the maintenance and inspection of manta ray anchors.
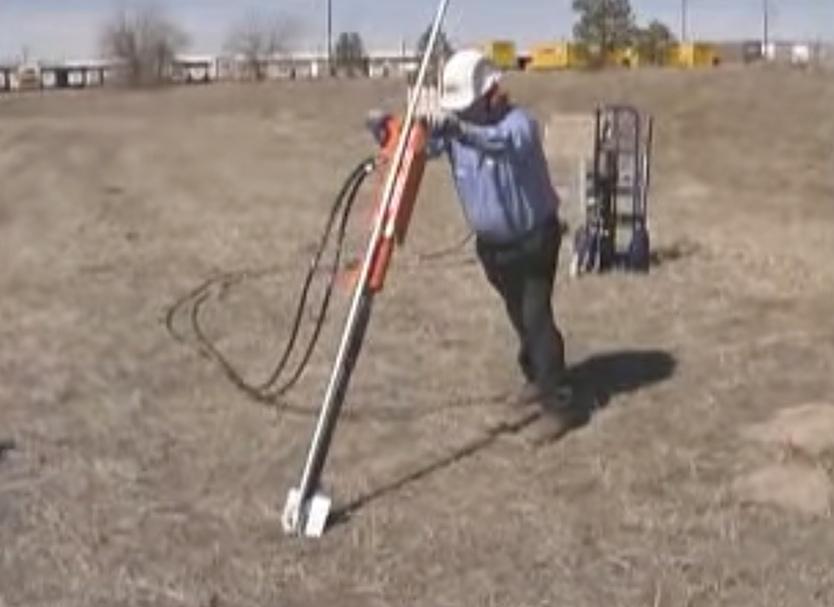

- Conduct regular visual inspections of the anchor and check for signs of damage, corrosion or wear.
- Perform detailed inspections and examine the condition of the anchor flukes and base plate. Check for proper alignment and depth of the anchor.
- Consider periodic load testing to ensure the anchor withstands the expected loads due to the extreme weather conditions.
- Apply suitable coatings to protect the anchor’s surface from corrosion and replace any damages components.
- Regularly inspect the soil conditions and ground settlement around the anchors and check for signs of soil erosion.
- Maintain detailed records of all inspections, maintenance activities and load testing results. This is including photographs and any observations taken.
Comparative analysis for manta ray in Southeast Asia
A comparative analysis includes assessing the different types, effectiveness and advantages of each manta ray anchor. There are various factors that influence the performance of the manta ray anchors. A comparative analysis in Southeast Asia requires specific data and case studies from each country in the region. The following are the commo factors to include in a comparative analysis in Southeast Asia.

- Functions – manta ray finds use in various industries in Southeast Asia such as renewable energy, marine and coastal infrastructure.
- Effectiveness – the anchors are effective in providing stability and load-bearing capacity even in areas with soft and sandy soils.
- Challenges – evaluate the advantages of the anchor in terms of environmental impact, regulatory compliance and maintenance in tropical climates.
- Regional variation – each country has specific applications and preferences for anchor types due to various factors.
- Local expertise – the installation, maintenance and inspections of the anchors require skills and profession. This local expertise may vary depending on the specific country in the region.
- Costs – compare the costs of Manta Ray anchors which depend on local labor costs and material availability.
- Growth – the increased expansion of infrastructure and urbanization increases the demand for manta ray anchors.
- Initiatives – the increased development of sustainable energy in Southeast Asia may drive the adoption of manta ray anchors.
Certification and standards in Southeast Asia
There are several certifications and standards that govern the use of manta ray anchor in Southeast Asia. These standards and certifications vary depending on country and region. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with the engineers and local authorities to ensure compliance with all relevant standards. Standards and certifications also help to ensure safety and reliability of the installations. The following are the common standards and certifications in Southeast Asia.

- International standards – the anchors are mostly manufactured and tested in accordance with international standards recognized worldwide.
- National standards – each country has their own set of standards related to anchor systems.
- Geotechnical engineering standards – these relate to soil conditions and anchor design to help ensure they are suitable for specific soil types.
- Corrosion protection standards – corrosion protection helps ensure the longevity of manta ray anchors used.
- Safety standards – safety standards help ensure the safety of workers and the public during the installation process.
- Load testing standards – this helps to verify the capacity of the anchors to withstand the expected loads.
- Certification and testing – proof of certifications from the manufacturer provides assurance of product quality and performance.
- Local regulations – local regulations vary depending on the country and application.
Regional market for manta ray anchor in southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is one of the fast-growing economies in the world which will increase the demand for anchors. This is from various factors such as infrastructure development, integration for renewable energy and need for reliable energy production. The leading countries for manta ray market include Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam. The following are the common factors influencing the regional market for manta ray anchors in Southeast Asia.

- Government policies – these initiatives support infrastructure development and renewable energy projects. This in turn leads to the increased demand for manta ray anchors.
- Local manufacturers – some of the countries have local manufacturers for manta ray anchors. They help to meet the growing local and domestic demand of the anchors.
- Imported products – some of the countries may import manta ray anchors rom international manufacturers. This depends on costs, availability and quality.
- Regulatory environment – compliance with local standards helps to increase safety of the products in various applications.
- Market size and growth – the market depends on the volume of infrastructure and construction projects in the region.
- Technological advancements – advances in anchor designs lead to the introduction of more efficient and durable anchor products.
- Market entry strategies – new manufacturers may need to establish partnerships with local distributors to enter the market.