
Pin insulator is a type of insulator used to support and insulate electrical conductors. It is also known as a spool insulator or line post. The main function of the pin insulator is to maintain a physical and electrical separation between the live conductor and the supporting structure. They are from materials such as porcelain, glass or composite. These materials help ensure the proper insulation to the conductors. The materials also are well suited for the diverse environmental conditions in Southeast Asia. Common types of pin insulators include hybrid, non-ceramic and polymer pin insulators. They find use in applications such as transmission lines, distribution lines, lighting arrestors and telecommunication lines.
Key features of pin insulator
The pin insulators have various features that help them improve the safety and reliability of the transmission lines. These features depend on the voltage levels, environmental conditions and mechanical loads of the application. The following are the key features of the pin insulators.
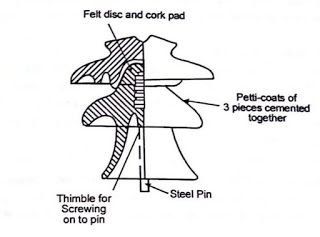
- Insulating materials – the materials depend on voltage rating, pollution levels and mechanical requirements. These materials include glass, porcelain and composite materials.
- High dielectric strength – they have a high dielectric strength. This allows them to withstand high electrical voltages. It does this without breaking down or allowing current to pass through.
- Mechanical strength – they also have strong mechanical properties. This is to support the weight of conductors and withstand wind loads.
- Weather resistance – the design withstands various weather conditions in the region. These include rain, snow, ice, UV radiation and temperature fluctuations.
- Pollution resistance – some insulators are able to resist pollution and reduce surface tracking or flashovers.
- Easy installation – the insulators are easy to install onto crossarms using a threaded pin at the top.
- Ease of maintenance – they are also easy to clean and maintain which ensures their continued performance.
- Voltage rating – they are also available in various ratings to match the requirements of different transmission and distribution systems.
- Safety – the design ensures they do not conduct electricity to the supporting structures. This helps to reduce the risk of electrical accidents.
Selection and maintenance of pin insulator
The selection of a pin insulator is a critical process as it involves considering several factors. These factors ensure the insulator meet the specific requirements of the system. These include voltage levels, environmental conditions, mechanical loads, material type, shed design and cost effectiveness. The installation process requires attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols. It also varies depending on the type of pin insulator, design of the supporting structure and local regulations. The following is a basic installation guide of the pin insulator.
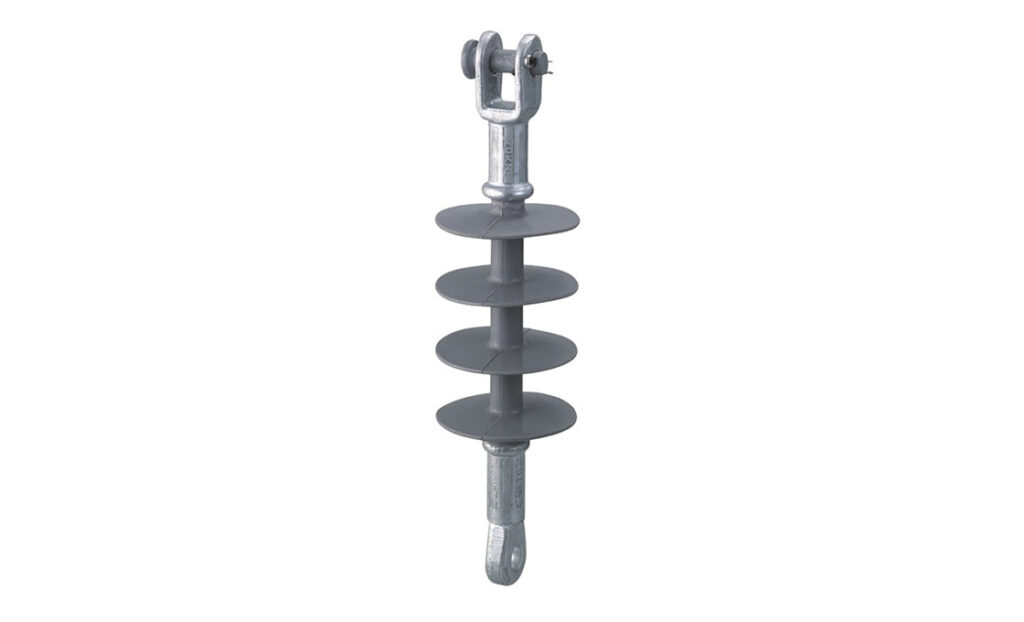

- Safety precautions – ensure you have all the safety personnel gear before the installation. Ensure the installation site is clear of any potential hazards.
- Materials and tools – ensure you have all the necessary materials and tools. This is including the pin insulators, insulator pins, locknuts, washers and mounting hardware. Inspect them for any visible defects or damage before the installation.
- Prepare the support structure – ensure the crossarm is securely attached to the transmission pole. Ensure it is clean and free from any contaminants that could affect the performance.
- Thread the insulator pin – thread the insulator pin into the central hole of the pin insulator.
- Mount the insulator – position the pin insulator on the crossarm in the desired location. The threaded end of the pin should insert through the hole in the crossarm. Place the washers and locknuts onto the threaded end of the pin below the crossarm.
- Alignment and leveling – ensure that the insulator aligns with the conductor and any other insulators.
- Torque the locknuts – use a torque wrench to tighten the locknuts to the manufacturers recommended specifications.
- Inspect the installation – visually inspect the entire installation to confirm that all components align, secure and free from any defects.
- Documentation – keep detailed records of the installation. This is including the type and location of the insulators.
Maintenance and inspection of pin insulator in Southeast Asia
Pin insulators require regular maintenance and inspection. This is to ensure the continued reliability and safe operation of the system. It also helps identify and address issues before they lead to insulator failures or electrical outages. The tropical climates in Southeast Asia requires the regular and proper maintenance and inspection of the pin insulators. The following is a basic guide on the maintenance and inspection in Southeast Asia.

- Perform regular visual inspections and check for signs of damage, cracks, chips or surface contamination on the insulator housing.
- Clean the insulators to remove dirt, dust and pollutants that can compromise their insulating properties. Use water and a soft sponge to clean the insulator surface gently.
- Inspect the insulator for signs of electrical flashover which leaves carbon tracks or deposits on the surface.
- Examine the fittings, pins, locknuts and washers for signs of corrosion, wear or damage. Ensure all the hardware components are securely fastened and in good conditions.
- Check for signs of pollution deposits or tracking on the insulator surface and monitor their performance.
- Check the torque of locknuts on the insulator pins to ensure they remain properly tightened.
- Maintain detailed records of insulator inspections, cleaning and maintenance activities. This includes any findings, actions taken and the date of each inspection.
Comparative analysis in Southeast Asian markets
Conducting a comparative analysis in Southeast Asian markets reveals several key factors that influence their use and selection in this region. The region has diverse environmental conditions, voltage levels and infrastructure development. These factors impact the choice of pin insulators in Southeast Asia. Conducting a comparative analysis also balances performance, safety and affordability. This is to ensure reliable electrical power transmission and distribution. The following are the factors to include in a comparative analysis of pin insulators in Southeast Asia.

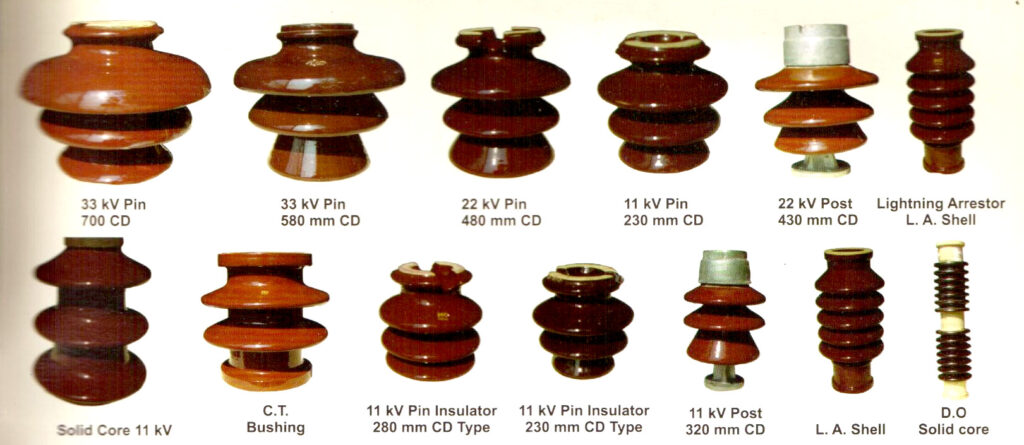
- Material type – main materials for used to make the pin insulators include porcelain, composite or glass materials. Assess the benefits of each material to the diverse weather conditions in Southeast Asia.
- Pollution resistance – areas with heavy pollution such as urban and industrial regions demand the use of resistant insulators. These may include composite or silicone rubber types.
- Voltage levels – there is a mix of low, medium and high voltage electrical systems in Southeast Asia. This requires proper selection of the insulator pins.
- Environmental conditions – the region has tropical climates with high humidity to coastal areas prone to salt spray. The selected pin insulator should withstand these conditions.
- Infrastructure development – the increased development in Southeast Asia leads to increased demand for pin insulators. This is to support expanding electrical grids in urban areas.
- Cost consideration – the choice of the pin insulator should balance the performance and budget.
Certifications and standards in Southeast Asia
Pin insulators should adhere to certifications and standard regulations in Southeast Asia. This is to ensure the quality, safety and reliability of the components in electrical transmission and distribution systems. The standards vary from one Asian country to another and are as discussed below.

- IEC standards – this standard provides the requirements for insulators, definitions, test methods and acceptance criteria.
- ASTM international standards – these standards provide guidance on test methods and standard specifications.
- ISO – this standard offers guidance on quality management systems and environmental management systems.
- Local or national standards – the countries in this region have their own national standards for electrical insulators.
- IECEE CB scheme – this scheme provides international certifications for electrical and electronic products.
- Safety and quality certifications – certifications from recognized safety and quality assessment organizations.
Regional market for pin insulator in Southeast Asia
There are various factors that influence the demand and market for pin insulators in southeast Asia. Some of these include diverse electrical infrastructure needs, environmental conditions and economic developments. The following is an overview of the regional market for pin insulators in Southeast Asia.

- Increased demand for pin insulators is from the increasing investments in electrical infrastructure, urbanization and economic development on the region.
- The regions electrical infrastructure of low, medium and high voltage influences the demand for different types and voltage classes of pin insulators.
- The environmental conditions such as tropical climates with high humidity to coastal areas demands the use of corrosion resistant insulators.
- The construction of new transmission and distribution lines contributes to the demand for pin insulators.
- Increased adoption of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power require the use of pin insulators.
- Economic growth and industrialization influence the demand for electricity and the demand for pin insulators.